mirror of https://github.com/OpenIPC/wiki.git
typo and markdown syntax
parent
c8b2451bc9
commit
d5db12be39
|
|
@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ Copy Server URL and Stream key from Settings.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Open `/etc/majestic.yaml` on camera and add the URL and the key into `outgoing` section of the config.
|
Open `/etc/majestic.yaml` on camera and add the URL and the key into `outgoing` section of the config.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Note:** Dont forget add `-` sign before paramethers!
|
**Note:** Dont forget add `-` sign before parameters!
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Note:** `outgoing` section may affect another section addition. Remember it!
|
**Note:** `outgoing` section may affect another section addition. Remember it!
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ For XM vendor boards with NT98562 and NT98566 SoC ONLY!!!
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Initial device firmware update
|
### Initial device firmware update
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**This section will be completed at the end of the research**
|
> **This section will be completed at the end of the research**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
run uk; run ur; reset # Flash kernel, rootfs and reboot device
|
run uk; run ur; reset # Flash kernel, rootfs and reboot device
|
||||||
|
|
@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ run uk; run ur; reset
|
||||||
### Notes
|
### Notes
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
After you have finished flashing new firmware, please run `firstboot` command
|
After you have finished flashing new firmware, please run `firstboot` command
|
||||||
to format jffs2 partition used to store settings.
|
to format `jffs2` partition used to store settings.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Known issues
|
### Known issues
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ run uk; run ur; reset
|
||||||
### Notes
|
### Notes
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
After you have finished flashing new firmware, please run `firstboot` command
|
After you have finished flashing new firmware, please run `firstboot` command
|
||||||
to format jffs2 partition used to store settings.
|
to format `jffs2` partition used to store settings.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Other info
|
### Other info
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ Follow the [Docker installation instructions][1].
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Create Docker image files
|
### Create Docker image files
|
||||||
Create a file named `Dockerfile` with the following content:
|
Create a file named `Dockerfile` with the following content:
|
||||||
```
|
```dockerfile
|
||||||
FROM debian:latest
|
FROM debian:latest
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
ARG DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
ARG DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||||
|
|
@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ services:
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Start the container
|
### Start the container
|
||||||
```
|
```bash
|
||||||
docker-compose up -d
|
docker-compose up -d
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
Docker will build an image if necessary and launch it in the background. During
|
Docker will build an image if necessary and launch it in the background. During
|
||||||
|
|
@ -49,11 +49,11 @@ building the container, Docker will also create `tftp/` subdirectory from which
|
||||||
your files will be served. Docker acts as user `systemd-network` from group
|
your files will be served. Docker acts as user `systemd-network` from group
|
||||||
`input` to access that directory. If you want to allow saving files sent via
|
`input` to access that directory. If you want to allow saving files sent via
|
||||||
TFTP to your machine you'll need to change ownership on that directory:
|
TFTP to your machine you'll need to change ownership on that directory:
|
||||||
```
|
```bash
|
||||||
sudo chown systemd-network:input ./tftp
|
sudo chown systemd-network:input ./tftp
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
Alternatively, you may loosen permissions on that directory:
|
Alternatively, you may loosen permissions on that directory:
|
||||||
```
|
```bash
|
||||||
sudo chmod 777 ./tftp
|
sudo chmod 777 ./tftp
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
Use your computer's IP address to access the TFTP server from other machines on
|
Use your computer's IP address to access the TFTP server from other machines on
|
||||||
|
|
@ -61,7 +61,7 @@ your local network.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Stop the container
|
### Stop the container
|
||||||
To stop the container and free up memory just run
|
To stop the container and free up memory just run
|
||||||
```
|
```bash
|
||||||
docker-compose stop
|
docker-compose stop
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
The container will be saved on your computer until the next time you need to
|
The container will be saved on your computer until the next time you need to
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1,4 +1,5 @@
|
||||||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[Table of Content](../README.md)
|
[Table of Content](../README.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Available Installation Methods
|
Available Installation Methods
|
||||||
|
|
@ -26,7 +27,7 @@ OpenIPC firmware installation using Coupler.
|
||||||
--------------------------------------------
|
--------------------------------------------
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Instructions for using [Coupler](https://github.com/openipc/coupler/) can be
|
Instructions for using [Coupler](https://github.com/openipc/coupler/) can be
|
||||||
found in [the project's documenation](https://github.com/openipc/coupler/).
|
found in [the project's documentation](https://github.com/openipc/coupler/).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
OpenIPC firmware installation via TFTP and UART, step by step.
|
OpenIPC firmware installation via TFTP and UART, step by step.
|
||||||
--------------------------------------------------------------
|
--------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||||
|
|
@ -34,7 +35,7 @@ OpenIPC firmware installation via TFTP and UART, step by step.
|
||||||
### Step 1. Determine the System on Chip.
|
### Step 1. Determine the System on Chip.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The SoC includes the CPU core of the camera, as well as all the necessary
|
The SoC includes the CPU core of the camera, as well as all the necessary
|
||||||
periperhals such as the camera and network interfaces. For various reasons
|
peripherals such as the camera and network interfaces. For various reasons
|
||||||
(including the limited onboard storage space on most IP Cameras), the OpenIPC
|
(including the limited onboard storage space on most IP Cameras), the OpenIPC
|
||||||
project currently builds separate firmware binaries for each SoC model. **You
|
project currently builds separate firmware binaries for each SoC model. **You
|
||||||
must identify the SoC which your camera uses**, so that you can use the correct
|
must identify the SoC which your camera uses**, so that you can use the correct
|
||||||
|
|
@ -65,7 +66,7 @@ retrieving bootable images from a designated boot server on the local network.
|
||||||
most likely already exists in distro's repo, and you only need to install it and
|
most likely already exists in distro's repo, and you only need to install it and
|
||||||
set it up.
|
set it up.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```bash
|
||||||
sudo apt install tftpd-hpa
|
sudo apt install tftpd-hpa
|
||||||
sudo sed -i '/^TFTP_OPTIONS/s/"$/ --create"/' /etc/default/tftpd-hpa
|
sudo sed -i '/^TFTP_OPTIONS/s/"$/ --create"/' /etc/default/tftpd-hpa
|
||||||
sudo systemctl restart tftpd-hpa.service
|
sudo systemctl restart tftpd-hpa.service
|
||||||
|
|
@ -114,27 +115,37 @@ application and connect to your adapter. Set your terminal settings to
|
||||||
Here's a few command lines for various terminal programs with session logging. Pick your poison.
|
Here's a few command lines for various terminal programs with session logging. Pick your poison.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### screen
|
#### screen
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Start a sessions with
|
Start a sessions with
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
screen -L -Logfile ipcam-$(date +%s).log /dev/ttyUSB0 115200
|
screen -L -Logfile ipcam-$(date +%s).log /dev/ttyUSB0 115200
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Use `Ctrl-a` followed by `\` to exit the session.
|
Use `Ctrl-a` followed by `\` to exit the session.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### minicom
|
#### `minicom`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Start a sessions with
|
Start a sessions with
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
minicom -b 115200 -8 --capturefile=ipcam-$(date +%s).log --color=on -D /dev/ttyUSB0
|
minicom -b 115200 -8 --capturefile=ipcam-$(date +%s).log --color=on -D /dev/ttyUSB0
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Use `Ctrl-a` followed by `x` to exit the session.
|
Use `Ctrl-a` followed by `x` to exit the session.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### picocom
|
#### `picocom`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Start a sessions with
|
Start a sessions with
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
picocom -b 115200 --databits 8 --parity n --stopbits 1 --flow n --logfile=ipcam-$(date +%s).log /dev/ttyUSB0
|
picocom -b 115200 --databits 8 --parity n --stopbits 1 --flow n --logfile=ipcam-$(date +%s).log /dev/ttyUSB0
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Use `Ctrl-a` followed by `Ctrl-x` to exit the session.
|
Use `Ctrl-a` followed by `Ctrl-x` to exit the session.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### PuTTY
|
#### PuTTY
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
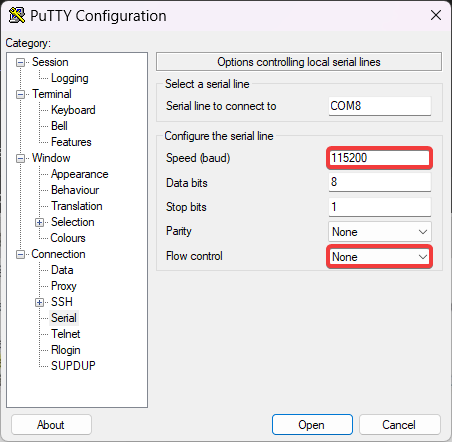
If you opt for a GUI terminal, namely [PuTTY](https://www.putty.org/), this is how it should look like:
|
If you opt for a GUI terminal, namely [PuTTY](https://www.putty.org/), this is how it should look like:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
@ -187,7 +198,7 @@ Most IP cameras nowadays are equipped with 8 or 16 MB NOR or NAND flash memory.
|
||||||
You can check the type and size of the chip installed on of your camera in the
|
You can check the type and size of the chip installed on of your camera in the
|
||||||
bootloader log output. You'll see something like this:
|
bootloader log output. You'll see something like this:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```console
|
||||||
U-Boot 2010.06-svn (Oct 21 2016 - 11:21:29)
|
U-Boot 2010.06-svn (Oct 21 2016 - 11:21:29)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Check Flash Memory Controller v100 ... Found
|
Check Flash Memory Controller v100 ... Found
|
||||||
|
|
@ -199,7 +210,7 @@ SPI Nor total size: 16MB
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Another example:
|
Another example:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```console
|
||||||
U-Boot 2013.07 (Feb 27 2019 - 02:05:08)
|
U-Boot 2013.07 (Feb 27 2019 - 02:05:08)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
DRAM: 64 MiB
|
DRAM: 64 MiB
|
||||||
|
|
@ -233,7 +244,7 @@ the values by `setenv` command (use IP addresses and netmask corresponding to
|
||||||
your local network), then save the new values into environment with `saveenv`
|
your local network), then save the new values into environment with `saveenv`
|
||||||
command.
|
command.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```bash
|
||||||
setenv ipaddr 192.168.1.253
|
setenv ipaddr 192.168.1.253
|
||||||
setenv netmask 255.255.255.0
|
setenv netmask 255.255.255.0
|
||||||
setenv gatewayip 192.168.1.1
|
setenv gatewayip 192.168.1.1
|
||||||
|
|
@ -294,7 +305,7 @@ If you followed step 2, you've got your own TFTP server serving files from
|
||||||
`/srv/tftp` directory. Extract files from the bundle you just downloaded into
|
`/srv/tftp` directory. Extract files from the bundle you just downloaded into
|
||||||
that directory.
|
that directory.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```bash
|
||||||
sudo tar -C /srv/tftp/ -xvf openipc.*.tgz
|
sudo tar -C /srv/tftp/ -xvf openipc.*.tgz
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -333,7 +344,7 @@ firmware. Welcome to OpenIPC!
|
||||||
After the first boot with the new firmware you need to clean the overlay
|
After the first boot with the new firmware you need to clean the overlay
|
||||||
partition. Run this in your terminal window:
|
partition. Run this in your terminal window:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```bash
|
||||||
firstboot
|
firstboot
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -85,18 +85,18 @@ RJ-45 connectors and wires.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
* __YouTube Streaming__
|
* __YouTube Streaming__
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### MiniHttp is the main streamer of the OpenIPC based system
|
### MiniHttp is the main streamer of the OpenIPC based system
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
It is important to tune configuration of MiniHttp by turning off unneeded
|
It is important to tune configuration of MiniHttp by turning off unneeded
|
||||||
protocols and features for better security and performance.
|
protocols and features for better security and performance.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Config file is located in `/etc/minihttp.ini`
|
Config file is located in `/etc/minihttp.ini`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### Debug mode:
|
### Debug mode:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```killall -sigint minihttp; sleep 1; export SENSOR=`ipctool --sensor_id`; minihttp```
|
```killall -sigint minihttp; sleep 1; export SENSOR=`ipctool --sensor_id`; minihttp```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### Production mode:
|
### Production mode:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```killall -sigint minihttp; sleep 1; export SENSOR=`ipctool --sensor_id`; minihttp 2>&1 | logger -p daemon.info -t minihttp &```
|
```killall -sigint minihttp; sleep 1; export SENSOR=`ipctool --sensor_id`; minihttp 2>&1 | logger -p daemon.info -t minihttp &```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -190,7 +190,6 @@ if(pinfo->mem->start = 0x20250000 /* address i2c-2 */) {
|
||||||
### Groups in Telegram related to development:
|
### Groups in Telegram related to development:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Tools used in Research and Development
|
## Tools used in Research and Development
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[hisi-trace](https://github.com/OpenIPC/hisi-trace) --> tool to run Sofia inside
|
[hisi-trace](https://github.com/OpenIPC/hisi-trace) --> tool to run Sofia inside
|
||||||
|
|
@ -209,7 +208,7 @@ Different hack & mod related to IP Cameras forums:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Below are some examples how to record video streams with various utilities.
|
Below are some examples how to record video streams with various utilities.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### gstreamer
|
### gstreamer
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
* rtsp h264 stream:
|
* rtsp h264 stream:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -219,9 +218,9 @@ Below are some examples how to record video streams with various utilities.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`gst-launch-1.0 rtspsrc location=rtsp://192.168.1.10:554/stream=0 ! rtpjitterbuffer ! rtph265depay ! h265parse ! mp4mux ! filesink location=stream0_h265.mp4 -e`
|
`gst-launch-1.0 rtspsrc location=rtsp://192.168.1.10:554/stream=0 ! rtpjitterbuffer ! rtph265depay ! h265parse ! mp4mux ! filesink location=stream0_h265.mp4 -e`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### ffmpeg
|
### ffmpeg
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### vlc
|
### vlc
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## How to login inside original firmware
|
## How to login inside original firmware
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -6,7 +6,6 @@ Introduction
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This page describes OpenWRT-based firmware variant.
|
This page describes OpenWRT-based firmware variant.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Firmware features
|
### Firmware features
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
* RTSP, ONVIF, NETIP
|
* RTSP, ONVIF, NETIP
|
||||||
|
|
@ -51,13 +50,13 @@ Unneeded options can be turned off for better security and performance.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
To run `majestic` in debug mode:
|
To run `majestic` in debug mode:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```bash
|
||||||
killall -sigint majestic; export SENSOR=$(ipctool --sensor_id); majestic
|
killall -sigint majestic; export SENSOR=$(ipctool --sensor_id); majestic
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
To run `majestic` in production mode restart the camera or run command:
|
To run `majestic` in production mode restart the camera or run command:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```bash
|
||||||
killall -sigint majestic; export SENSOR=$(ipctool --sensor_id); majestic 2>&1 | logger -p daemon.info -t majestic &
|
killall -sigint majestic; export SENSOR=$(ipctool --sensor_id); majestic 2>&1 | logger -p daemon.info -t majestic &
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -124,7 +123,7 @@ cd OpenIPC
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Use Docker for building
|
### Use Docker for building
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Default Dockerfile.openipc**
|
> **Default Dockerfile.openipc**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```docker
|
```docker
|
||||||
FROM debian:stretch
|
FROM debian:stretch
|
||||||
|
|
@ -147,7 +146,7 @@ RUN ./Project_OpenIPC.sh update
|
||||||
RUN ./Project_OpenIPC.sh 18ev200_DEFAULT # <= Change this ID to you profile
|
RUN ./Project_OpenIPC.sh 18ev200_DEFAULT # <= Change this ID to you profile
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Start building**
|
> **Start building**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
#!/bin/bash
|
#!/bin/bash
|
||||||
|
|
@ -503,7 +502,7 @@ flash partitions from shell command line:
|
||||||
flashcp -v openwrt-hi35xx-XXXXX-u-boot.bin boot
|
flashcp -v openwrt-hi35xx-XXXXX-u-boot.bin boot
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**or**
|
> **or**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
flashcp -v openwrt-hi35xx-XXXXX-u-boot.bin /dev/mtd0
|
flashcp -v openwrt-hi35xx-XXXXX-u-boot.bin /dev/mtd0
|
||||||
|
|
@ -539,7 +538,7 @@ reboot
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Installing the original MAC
|
### Installing the original MAC
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**U-boot ENV and Linux UCI**
|
> **U-boot ENV and Linux UCI**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```txt
|
```txt
|
||||||
fw_setenv ethaddr 00:01:02:03:04:05
|
fw_setenv ethaddr 00:01:02:03:04:05
|
||||||
|
|
@ -550,7 +549,7 @@ uci commit
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Installing the correct sensor
|
### Installing the correct sensor
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Specify your correct sensor, control type, and data bus**
|
> **Specify your correct sensor, control type, and data bus**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```txt
|
```txt
|
||||||
fw_setenv sensor imx291_i2c_lvds
|
fw_setenv sensor imx291_i2c_lvds
|
||||||
|
|
@ -565,7 +564,7 @@ If something went wrong, you can reset configuration to defaults.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Clean overlayfs (reset)
|
### Clean overlayfs (reset)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Restore to default Linux settings**
|
> **Restore to default Linux settings**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```txt
|
```txt
|
||||||
firstboot
|
firstboot
|
||||||
|
|
@ -575,7 +574,7 @@ reboot
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Clean u-boot env
|
### Clean u-boot env
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Restore to default u-boot env**
|
> **Restore to default u-boot env**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```txt
|
```txt
|
||||||
flash_eraseall -j /dev/$(awk -F ':' '/env/ {print $1}' /proc/mtd)
|
flash_eraseall -j /dev/$(awk -F ':' '/env/ {print $1}' /proc/mtd)
|
||||||
|
|
@ -587,7 +586,7 @@ reboot
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
If something goes horribly wrong, and you want your backed up firmware back
|
If something goes horribly wrong, and you want your backed up firmware back
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Restore backup up firmware via serial**
|
> **Restore backup up firmware via serial**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Install kermit using [this instruction](https://glasstty.com/?p=662) or similar.
|
Install kermit using [this instruction](https://glasstty.com/?p=662) or similar.
|
||||||
Here are the sample commands for 8MB Flash.
|
Here are the sample commands for 8MB Flash.
|
||||||
|
|
@ -625,11 +624,11 @@ OpenIPC # sf write 0x82000000 0x0 ${filesize}
|
||||||
Writing at 0x800000 -- 100% complete.
|
Writing at 0x800000 -- 100% complete.
|
||||||
OpenIPC #
|
OpenIPC #
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
**Restore backup up firmware via TFTP**
|
> **Restore backup up firmware via TFTP**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Here are the commands for 8MB Flash.
|
Here are the commands for 8MB Flash.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```shell
|
||||||
setenv ipaddr 192.168.1.10
|
setenv ipaddr 192.168.1.10
|
||||||
setenv serverip 192.168.1.254
|
setenv serverip 192.168.1.254
|
||||||
sf probe 0; sf lock 0
|
sf probe 0; sf lock 0
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -10,9 +10,10 @@ hash of that password while extracting a copy of the firmware image.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Password hash
|
### Password hash
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```console
|
||||||
$1$bh2njiGH$4duacOMcXDh6myANzbZTf.
|
$1$bh2njiGH$4duacOMcXDh6myANzbZTf.
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The hashed salt password string consists of three parts: hashing algorithm
|
The hashed salt password string consists of three parts: hashing algorithm
|
||||||
identifier, salt and password hash, each of which is preceded by a dollar sign.
|
identifier, salt and password hash, each of which is preceded by a dollar sign.
|
||||||
The first part, `$1`, is the hashing algorithm encoded with one (rarely two)
|
The first part, `$1`, is the hashing algorithm encoded with one (rarely two)
|
||||||
|
|
@ -45,7 +46,8 @@ hours, especially using high-quality dictionaries.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
In the example above we used password "openipc". You can check the validity of
|
In the example above we used password "openipc". You can check the validity of
|
||||||
the password using either `mkpasswd` or `openssl`:
|
the password using either `mkpasswd` or `openssl`:
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
$ mkpasswd -m md5crypt -S bh2njiGH openipc
|
$ mkpasswd -m md5crypt -S bh2njiGH openipc
|
||||||
$1$bh2njiGH$4duacOMcXDh6myANzbZTf.
|
$1$bh2njiGH$4duacOMcXDh6myANzbZTf.
|
||||||
$ openssl passwd -1 -salt bh2njiGH openipc
|
$ openssl passwd -1 -salt bh2njiGH openipc
|
||||||
|
|
@ -57,6 +59,7 @@ researchers in the field could dedicate their cryptographic resources to
|
||||||
discover even more yet unknown passwords. Sharing is caring, boys!
|
discover even more yet unknown passwords. Sharing is caring, boys!
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Some passwords that we found in different firmware
|
### Some passwords that we found in different firmware
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
| Hash | Plain text |
|
| Hash | Plain text |
|
||||||
|---------------------------------------|------------|
|
|---------------------------------------|------------|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -100,7 +103,7 @@ discover even more yet unknown passwords. Sharing is caring, boys!
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Hijacking the default password
|
### Hijacking the default password
|
||||||
_tested on Goke_
|
> _tested on Goke_
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Over the UART interface, it is possible to temporarily interrupt the normal
|
Over the UART interface, it is possible to temporarily interrupt the normal
|
||||||
booting sequence and drop into a limited Linux shell at early stage of
|
booting sequence and drop into a limited Linux shell at early stage of
|
||||||
|
|
@ -142,7 +145,8 @@ file where password is written on every restart. Search for `/etc/passwd` and
|
||||||
change a letter in its name to something different, like `/etc/passwT`.
|
change a letter in its name to something different, like `/etc/passwT`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Pack the squash file system using `mksquashfs`:
|
Pack the squash file system using `mksquashfs`:
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
mksquashfs ./squashfs-root ./file -comp xz -no-xattrs -noappend -no-exports -all-root -quiet -b 131072
|
mksquashfs ./squashfs-root ./file -comp xz -no-xattrs -noappend -no-exports -all-root -quiet -b 131072
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
and copy it from the SD card back to `/rom` directory on the camera.
|
and copy it from the SD card back to `/rom` directory on the camera.
|
||||||
|
|
@ -161,6 +165,4 @@ you restart the device, you will have full working system with your own password
|
||||||
[2]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brute-force_attack
|
[2]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brute-force_attack
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
---------------------------------------------------
|
---------------------------------------------------
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
10
en/syslog.md
10
en/syslog.md
|
|
@ -10,9 +10,11 @@ There is no difficulty in this, you need to configure the server by enabling the
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Will start with the camera. Add the option -R server-ip:514 with the address as shown in the example and reboot the device.
|
Will start with the camera. Add the option -R server-ip:514 with the address as shown in the example and reboot the device.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
root@openipc-hi3516ev300:~# differ /etc/init.d/S01syslogd
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
root@openipc-hi3516ev300:~# differ /etc/init.d/S01syslogd.
|
|
||||||
|
```diff
|
||||||
--- /rom/etc/init.d/S01syslogd
|
--- /rom/etc/init.d/S01syslogd
|
||||||
+++ /etc/init.d/S01syslogd
|
+++ /etc/init.d/S01syslogd
|
||||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
|
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
|
||||||
|
|
@ -28,8 +30,7 @@ root@openipc-hi3516ev300:~# differ /etc/init.d/S01syslogd.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
In the server configuration file, write down the options of which port numbers and protocols to listen to it and make a restart of the service.
|
In the server configuration file, write down the options of which port numbers and protocols to listen to it and make a restart of the service.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```diff
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
--- rsyslog.conf.orig 2022-09-30 16:41:52.081353630 +0300
|
--- rsyslog.conf.orig 2022-09-30 16:41:52.081353630 +0300
|
||||||
+++ rsyslog.conf 2023-05-01 12:44:06.098032982 +0300
|
+++ rsyslog.conf 2023-05-01 12:44:06.098032982 +0300
|
||||||
@@ -14,12 +14,12 @@
|
@@ -14,12 +14,12 @@
|
||||||
|
|
@ -52,4 +53,3 @@ In the server configuration file, write down the options of which port numbers a
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Comments and additions welcome. Bye !
|
Comments and additions welcome. Bye !
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -7,7 +7,7 @@ Upgrading firmware
|
||||||
### Upgrading from GitHub
|
### Upgrading from GitHub
|
||||||
For old firmware running `sysupgrade` without parameters is enough. For newer firmware, run `sysupgrade -k -r` to update both kernel and rootfs.
|
For old firmware running `sysupgrade` without parameters is enough. For newer firmware, run `sysupgrade -k -r` to update both kernel and rootfs.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
__ATTENTION! Upgrading firmware can lead to "bricking" your camera. Make sure you are prepared both morally and skillwise. Have your rescue SD card and/or UART adapter ready. Be prepared to desolder and reprogram flash chip as the last resort. Do not upgrade production cameras unless you really have to!__
|
__ATTENTION! Upgrading firmware can lead to "bricking" your camera. Make sure you are prepared both morally and skillwise. Have your rescue SD card and/or UART adapter ready. Be prepared to de-solder and reprogram flash chip as the last resort. Do not upgrade production cameras unless you really have to!__
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Upgrading from a TFTP server
|
### Upgrading from a TFTP server
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -18,17 +18,20 @@ Extract content of the bundle into the root directory of your TFTP server.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
On the camera run:
|
On the camera run:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### From Linux
|
#### Github: From Linux
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
soc=$(fw_printenv -n soc)
|
soc=$(fw_printenv -n soc)
|
||||||
serverip=$(fw_printenv -n serverip)
|
serverip=$(fw_printenv -n serverip)
|
||||||
busybox tftp -r rootfs.squashfs.${soc} -g ${serverip}
|
busybox tftp -r rootfs.squashfs.${soc} -g ${serverip}
|
||||||
busybox tftp -r uImage.${soc} -g ${serverip}
|
busybox tftp -r uImage.${soc} -g ${serverip}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### Alternatively, from U-Boot
|
#### Github: Alternatively, from U-Boot
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
for 8MB image
|
for 8MB image
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
mw.b ${baseaddr} 0xff 0x200000
|
mw.b ${baseaddr} 0xff 0x200000
|
||||||
tftp ${baseaddr} uImage.${soc}
|
tftp ${baseaddr} uImage.${soc}
|
||||||
sf probe 0; sf erase 0x50000 0x200000; sf write ${baseaddr} 0x50000 ${filesize}
|
sf probe 0; sf erase 0x50000 0x200000; sf write ${baseaddr} 0x50000 ${filesize}
|
||||||
|
|
@ -37,8 +40,10 @@ mw.b ${baseaddr} 0xff 0x500000
|
||||||
tftp ${baseaddr} rootfs.squashfs.${soc}
|
tftp ${baseaddr} rootfs.squashfs.${soc}
|
||||||
sf probe 0; sf erase 0x250000 0x500000; sf write ${baseaddr} 0x250000 ${filesize}
|
sf probe 0; sf erase 0x250000 0x500000; sf write ${baseaddr} 0x250000 ${filesize}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
for 16MB image
|
for 16MB image
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
mw.b ${baseaddr} 0xff 0x300000
|
mw.b ${baseaddr} 0xff 0x300000
|
||||||
tftp ${baseaddr} uImage.${soc}
|
tftp ${baseaddr} uImage.${soc}
|
||||||
sf probe 0; sf erase 0x50000 0x300000; sf write ${baseaddr} 0x50000 ${filesize}
|
sf probe 0; sf erase 0x50000 0x300000; sf write ${baseaddr} 0x50000 ${filesize}
|
||||||
|
|
@ -48,39 +53,48 @@ tftp ${baseaddr} rootfs.squashfs.${soc}
|
||||||
sf probe 0; sf erase 0x350000 0xa00000; sf write ${baseaddr} 0x350000 ${filesize}
|
sf probe 0; sf erase 0x350000 0xa00000; sf write ${baseaddr} 0x350000 ${filesize}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Upgrading from local files
|
### Upgrading from local files
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Go to <https://github.com/OpenIPC/firmware/releases/tag/latest> and download the latest firmware bundle for your SoC.
|
Go to <https://github.com/OpenIPC/firmware/releases/tag/latest> and download the latest firmware bundle for your SoC.
|
||||||
Unpack the bundle and upload its content on camera using `scp`:
|
Unpack the bundle and upload its content on camera using `scp`:
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
tar xvf <firmware.tgz>
|
tar xvf <firmware.tgz>
|
||||||
scp uImage* rootfs* root@<yourcameraip>:/tmp/
|
scp uImage* rootfs* root@<yourcameraip>:/tmp/
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
On the camera run:
|
On the camera run:
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
soc=$(fw_printenv -n soc)
|
soc=$(fw_printenv -n soc)
|
||||||
sysupgrade --kernel=/tmp/uImage.${soc} --rootfs=/tmp/rootfs.squashfs.${soc} -z
|
sysupgrade --kernel=/tmp/uImage.${soc} --rootfs=/tmp/rootfs.squashfs.${soc} -z
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Upgrading from SD card
|
### Upgrading from SD card
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### From Linux
|
#### SD Card: From Linux
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Go to <https://github.com/OpenIPC/firmware/releases/tag/latest> and download the latest firmware bundle for your SoC.
|
Go to <https://github.com/OpenIPC/firmware/releases/tag/latest> and download the latest firmware bundle for your SoC.
|
||||||
Insert an SD card into your desktop PC. Unpack the bundle and copy its content to the card:
|
Insert an SD card into your desktop PC. Unpack the bundle and copy its content to the card:
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
tar xvf <firmware.tgz>
|
tar xvf <firmware.tgz>
|
||||||
cp uImage* rootfs* /media/<username>/<card-id>/
|
cp uImage* rootfs* /media/<username>/<card-id>/
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Insert the SD card into your camera.
|
Insert the SD card into your camera.
|
||||||
On the camera run:
|
On the camera run:
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
soc=$(fw_printenv -n soc)
|
soc=$(fw_printenv -n soc)
|
||||||
sysupgrade --kernel=/mnt/mmcblk0p1/uImage.${soc} --rootfs=/mnt/mmcblk0p1/rootfs.squashfs.${soc} --force_ver -z
|
sysupgrade --kernel=/mnt/mmcblk0p1/uImage.${soc} --rootfs=/mnt/mmcblk0p1/rootfs.squashfs.${soc} --force_ver -z
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### Alternatively, from U-Boot
|
#### SD Card: Alternatively, from U-Boot
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
for 8MB image
|
for 8MB image
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
mw.b ${baseaddr} 0xff 0x200000
|
mw.b ${baseaddr} 0xff 0x200000
|
||||||
fatload mmc 0:1 ${baseaddr} uImage.${soc}
|
fatload mmc 0:1 ${baseaddr} uImage.${soc}
|
||||||
sf probe 0; sf erase 0x50000 0x200000; sf write ${baseaddr} 0x50000 ${filesize}
|
sf probe 0; sf erase 0x50000 0x200000; sf write ${baseaddr} 0x50000 ${filesize}
|
||||||
|
|
@ -89,8 +103,10 @@ mw.b ${baseaddr} 0xff 0x500000
|
||||||
fatload mmc 0:1 ${baseaddr} rootfs.squashfs.${soc}
|
fatload mmc 0:1 ${baseaddr} rootfs.squashfs.${soc}
|
||||||
sf probe 0; sf erase 0x250000 0x500000; sf write ${baseaddr} 0x250000 ${filesize}
|
sf probe 0; sf erase 0x250000 0x500000; sf write ${baseaddr} 0x250000 ${filesize}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
for 16MB image
|
for 16MB image
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
mw.b ${baseaddr} 0xff 0x300000
|
mw.b ${baseaddr} 0xff 0x300000
|
||||||
fatload mmc 0:1 ${baseaddr} uImage.${soc}
|
fatload mmc 0:1 ${baseaddr} uImage.${soc}
|
||||||
sf probe 0; sf erase 0x50000 0x300000; sf write ${baseaddr} 0x50000 ${filesize}
|
sf probe 0; sf erase 0x50000 0x300000; sf write ${baseaddr} 0x50000 ${filesize}
|
||||||
|
|
@ -101,17 +117,23 @@ sf probe 0; sf erase 0x350000 0xa00000; sf write ${baseaddr} 0x350000 ${filesize
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Flashing U-Boot via ymodem
|
### Flashing U-Boot via ymodem
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Clean 320K of RAM amd load bootloader file into it:
|
Clean 320K of RAM amd load bootloader file into it:
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
mw.b ${baseaddr} 0xff 0x50000
|
mw.b ${baseaddr} 0xff 0x50000
|
||||||
loady
|
loady
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
_(press "Ctrl-a" followed by ":", then type)_
|
|
||||||
```
|
> _(press "Ctrl-a" followed by ":", then type)_
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
exec !! sz --ymodem u-boot.bin
|
exec !! sz --ymodem u-boot.bin
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
After the file if uploaded, write it into ROM:
|
After the file if uploaded, write it into ROM:
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
sf probe 0
|
sf probe 0
|
||||||
sf erase 0x0 0x50000
|
sf erase 0x0 0x50000
|
||||||
sf write ${baseaddr} 0x0 ${filesize}
|
sf write ${baseaddr} 0x0 ${filesize}
|
||||||
|
|
@ -120,10 +142,12 @@ sf write ${baseaddr} 0x0 ${filesize}
|
||||||
### Troubleshooting
|
### Troubleshooting
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
If you got this error:
|
If you got this error:
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
```console
|
||||||
losetup: /tmp/rootfs.squashfs.${soc}: No such file or directory
|
losetup: /tmp/rootfs.squashfs.${soc}: No such file or directory
|
||||||
Rootfs: Unable to get hostname, execution was interrupted...
|
Rootfs: Unable to get hostname, execution was interrupted...
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
then try to update only kernel first:
|
then try to update only kernel first:
|
||||||
`sysupgrade -k`
|
`sysupgrade -k`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -131,6 +155,7 @@ If it doesn't help, use `--force` option:
|
||||||
`sysupgrade -r --force`
|
`sysupgrade -r --force`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
If you caught a glitch, retrieve the most recent version of the utility:
|
If you caught a glitch, retrieve the most recent version of the utility:
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
curl -k -L -o /usr/sbin/sysupgrade "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/OpenIPC/firmware/master/general/overlay/usr/sbin/sysupgrade"
|
curl -k -L -o /usr/sbin/sysupgrade "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/OpenIPC/firmware/master/general/overlay/usr/sbin/sysupgrade"
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -5,7 +5,7 @@
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Some IP-cameras require additional parameters set to make the network interface work.
|
Some IP-cameras require additional parameters set to make the network interface work.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### For recent firmware
|
### For recent firmware
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Use `extras` boot variable. In Linux console run this
|
Use `extras` boot variable. In Linux console run this
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ fw_setenv extras 'hieth.mdioifu=1 hieth.mdioifd=1' && reboot
|
||||||
If nothing of the above worked for you, seek help on [our Telegram channel](https://t.me/openipc).
|
If nothing of the above worked for you, seek help on [our Telegram channel](https://t.me/openipc).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### For older firmware
|
### For older firmware
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Set `phyaddru` and `phyaddrd` variables from U-Boot console:
|
Set `phyaddru` and `phyaddrd` variables from U-Boot console:
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ Wi-Fi for XM530 based devices
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Save this script as `/usr/sbin/wifi`
|
Save this script as `/usr/sbin/wifi`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```bash
|
||||||
#!/bin/sh
|
#!/bin/sh
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
WIFI=$1
|
WIFI=$1
|
||||||
|
|
@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ fi
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Save these settings to `/etc/network/interfaces`
|
Save these settings to `/etc/network/interfaces`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```bash
|
||||||
auto eth2
|
auto eth2
|
||||||
iface eth2 inet dhcp
|
iface eth2 inet dhcp
|
||||||
pre-up wifi xm711
|
pre-up wifi xm711
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -9,7 +9,7 @@ Wireless settings
|
||||||
- Following packages are needed for the HI3516EV300 CamHi module.
|
- Following packages are needed for the HI3516EV300 CamHi module.
|
||||||
- The example build configuration is: `hi3516ev300_lite_defconfig`
|
- The example build configuration is: `hi3516ev300_lite_defconfig`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```shell
|
||||||
BR2_PACKAGE_WIRELESS_CONFIGURATION=y
|
BR2_PACKAGE_WIRELESS_CONFIGURATION=y
|
||||||
BR2_PACKAGE_WPA_SUPPLICANT_AP_SUPPORT=y
|
BR2_PACKAGE_WPA_SUPPLICANT_AP_SUPPORT=y
|
||||||
BR2_PACKAGE_MT7601U_AP_OPENIPC=y
|
BR2_PACKAGE_MT7601U_AP_OPENIPC=y
|
||||||
|
|
@ -72,13 +72,13 @@ fi
|
||||||
- For the initial setup, the device will create an access point with the name OpenIPC and password 12345678.
|
- For the initial setup, the device will create an access point with the name OpenIPC and password 12345678.
|
||||||
- After connecting to the device, credentials can be changed with the wireless script:
|
- After connecting to the device, credentials can be changed with the wireless script:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```shell
|
||||||
wireless setup [SSID] [PASS]
|
wireless setup [SSID] [PASS]
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- Additional settings are:
|
- Additional settings are:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```shell
|
||||||
wireless connect
|
wireless connect
|
||||||
wireless reset
|
wireless reset
|
||||||
wireless show
|
wireless show
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ for more information.
|
||||||
- switch "resolution" from "1080p" to "variable";
|
- switch "resolution" from "1080p" to "variable";
|
||||||
- switch "ingestionType" from "rtmp" to "hls":
|
- switch "ingestionType" from "rtmp" to "hls":
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```json
|
||||||
"cdn": {
|
"cdn": {
|
||||||
"ingestionType": "hls",
|
"ingestionType": "hls",
|
||||||
"frameRate": "variable",
|
"frameRate": "variable",
|
||||||
|
|
@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ for more information.
|
||||||
- 'scheduledEndTime' like '2020-04-21T01:00:00.000Z' (scheduled end time should be after the scheduled start time)
|
- 'scheduledEndTime' like '2020-04-21T01:00:00.000Z' (scheduled end time should be after the scheduled start time)
|
||||||
- also press blue plus button inside "snippet" block and add "channelId" with given from stream step value
|
- also press blue plus button inside "snippet" block and add "channelId" with given from stream step value
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```json
|
||||||
"snippet": {`
|
"snippet": {`
|
||||||
`"title": "My Hometown Camera",`
|
`"title": "My Hometown Camera",`
|
||||||
`"scheduledStartTime": "2021-04-12T00:00:00.000Z",`
|
`"scheduledStartTime": "2021-04-12T00:00:00.000Z",`
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue