mirror of https://github.com/OpenIPC/wiki.git
Merge branch 'master' into master
commit
a58c16611b
44
README.md
44
README.md
|
|
@ -1,44 +0,0 @@
|
|||
OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
============
|
||||
|
||||
[English](en/index.md) | [Русский](ru/index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> "Improving the world, one patch at a time."
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### This is an open project, so you can help, too.
|
||||
|
||||
We try to collect, organize and share as much information regarding different
|
||||
aspects of the project as we can. But sometimes we overlook things that seem
|
||||
obvious to us, developers, but are not so obvious to end-users, people who are
|
||||
less familiar with nuts and bolts behind the scene. That is why we set up this
|
||||
wiki and let anyone having a GitHub account to make additions and improvements
|
||||
to the knowledgebase.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to contribute.
|
||||
|
||||
Sign in into your GitHub account, or [get yourself one][gh-signup] if you don't
|
||||
have it yet. It's free.
|
||||
|
||||
Go to [the wiki repository](https://github.com/openIPC/wiki/) and fork it.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Make changes (correct a typo, add another record into a table, or write a new
|
||||
article) and commit them to your own fork of the repository.
|
||||
|
||||
From your repository, create a pull request, so we could review and incorporate
|
||||
your changes into our version of the wiki.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Small corrections, typos.
|
||||
|
||||
It is even easier to deal with small corrections while using GitHub. Spotted a
|
||||
typo? Have an idea of a better wording? Noticed a broken link? Just hit this
|
||||
pencil-looking button and make corrections.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[gh-signup]: https://github.com/signup
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
How to install HTTPS certificates on your camera
|
||||
------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## Board manufacturers
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## Company names
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -19,4 +19,3 @@
|
|||
- Shenzhen Zhongwei Century Technology Co., Ltd.
|
||||
- Shenzhen Hichip Vision Technology Co., Ltd.
|
||||
- Chengdu Powerview Science and Technology Co., Ltd.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
> "Improving the world, one patch at a time."
|
||||
|
||||
### This is an open project, so you can help, too.
|
||||
|
||||
We try to collect, organize and share as much information regarding different
|
||||
aspects of the project as we can. But sometimes we overlook things that seem
|
||||
obvious to us, developers, but are not so obvious to end-users, people who are
|
||||
less familiar with nuts and bolts behind the scene. That is why we set up this
|
||||
wiki and let anyone having a GitHub account to make additions and improvements
|
||||
to the knowledgebase.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to contribute.
|
||||
|
||||
Sign in into your GitHub account, or [get yourself one][gh-signup] if you don't
|
||||
have it yet. It's free.
|
||||
|
||||
Go to [the wiki repository](https://github.com/openIPC/wiki/) and fork it.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Make changes (correct a typo, add another record into a table, or write a new
|
||||
article) and commit them to your own fork of the repository.
|
||||
|
||||
From your repository, create a pull request, so we could review and incorporate
|
||||
your changes into our version of the wiki.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Small corrections, typos.
|
||||
|
||||
It is even easier to deal with small corrections while using GitHub. Spotted a
|
||||
typo? Have an idea of a better wording? Noticed a broken link? Just hit this
|
||||
pencil-looking button and make corrections.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[gh-signup]: https://github.com/signup
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
FFMPEG, RTSP and SRT examples
|
||||
-----------------------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Boot device with NFS
|
||||
--------------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Interesting tricks
|
||||
------------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
OpenIPC Developers
|
||||
------------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -4,27 +4,27 @@
|
|||
|
||||
[Product datasheet](https://chacon.com/datasharing/doc/IPCAM-RI01/ipcam-ri01_user_manual.pdf)
|
||||
|
||||
This camera is a rebrand of a manufacturing company identified by "PPStrong".
|
||||
This camera is a rebranding of a manufacturing company identified by "PPStrong".
|
||||
I'm sure there are other cameras out there that are using the same hardware (or similar with minor changes).
|
||||
|
||||
## Hardware
|
||||
|
||||
| System | Description |
|
||||
|--------|-------------------|
|
||||
| SoC | HI3518EV300 |
|
||||
| Sensor | JXF23 |
|
||||
| System | Description |
|
||||
|--------|--------------------------------------|
|
||||
| SoC | HI3518EV300 |
|
||||
| Sensor | JXF23 |
|
||||
| Flash | 16Mb (XM25QH128A) or 8Mb (XM25QH64A) |
|
||||
| WiFi | RTL8188FU |
|
||||
| WiFi | RTL8188FU |
|
||||
|
||||
#### OpenIPC status
|
||||
|
||||
| Component | Status |
|
||||
|-----------|--------|
|
||||
| WiFi | [Working](https://github.com/OpenIPC/firmware/issues/48) |
|
||||
| Motors | [Working](#motor-driver) (patched driver) |
|
||||
| Red/Blue leds | [Working](#leds) |
|
||||
| IR Led | Working |
|
||||
| IR Cut | Working |
|
||||
| Component | Status |
|
||||
|---------------|----------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| WiFi | [Working](https://github.com/OpenIPC/firmware/issues/48) |
|
||||
| Motors | [Working](#motor-driver) (patched driver) |
|
||||
| Red/Blue LEDs | [Working](#leds) |
|
||||
| IR LED | Working |
|
||||
| IR Cut | Working |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Hardware details
|
||||
|
|
@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ The camera mainboard is identified by "SPEED5S-H1MB_F23".
|
|||
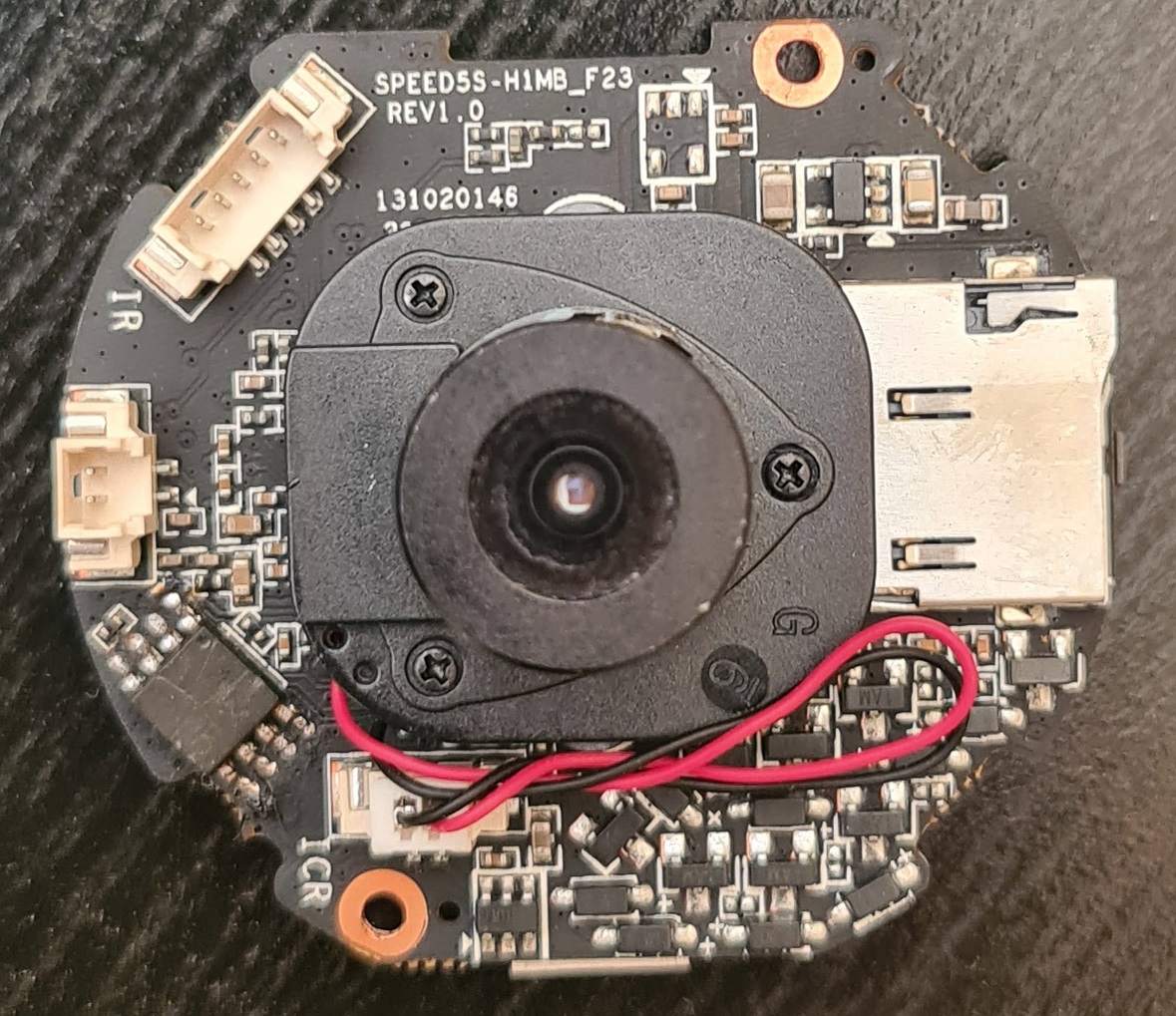
|
||||
At the top of the mainboard:
|
||||
- a micro sdcard slot on the right
|
||||
- connector labeled "IR" powers the IR led, a red led and a blue led
|
||||
- connector labeled "IR" powers the IR LED, a red LED and a blue LED
|
||||
- connector "ICR" powers the IR cut filter
|
||||
- non-identified connector is an input for the microphone
|
||||
- SPI NOR flash chip (QH128A)
|
||||
|
|
@ -83,24 +83,24 @@ At the bottom of the mainboard:
|
|||
|
||||
### GPIOs
|
||||
|
||||
| nr | Description |
|
||||
|-----|-------------|
|
||||
| 0x0f (15) | irCut_1 |
|
||||
| 0x0c (12) | irCut_2 |
|
||||
| 0x28 (40) | IR Led |
|
||||
| 0x33 (51) | Red Led |
|
||||
| 0x32 (50) | Blue Led |
|
||||
| 0x0d (13) | wlan power |
|
||||
| 0x00 (0) | AcShdn |
|
||||
| 0x09 (9) | Reset button |
|
||||
| nr | Description |
|
||||
|-----------|---------------|
|
||||
| 0x0f (15) | irCut_1 |
|
||||
| 0x0c (12) | irCut_2 |
|
||||
| 0x28 (40) | IR LED |
|
||||
| 0x33 (51) | Red LED |
|
||||
| 0x32 (50) | Blue LED |
|
||||
| 0x0d (13) | wlan power |
|
||||
| 0x00 (0) | AcShdn |
|
||||
| 0x09 (9) | Reset button |
|
||||
| 0x3b (59) | Tilt motor A1 |
|
||||
| 0x3a (58) | Tilt motor A2 |
|
||||
| 0x39 (57) | Tilt motor B1 |
|
||||
| 0x38 (56) | Tilt motor B2 |
|
||||
| 0x47 (71) | Pan motor A1 |
|
||||
| 0x45 (69) | Pan motor A2 |
|
||||
| 0x46 (70) | Pan motor B1 |
|
||||
| 0x44 (68) | Pan motor B2 |
|
||||
| 0x47 (71) | Pan motor A1 |
|
||||
| 0x45 (69) | Pan motor A2 |
|
||||
| 0x46 (70) | Pan motor B1 |
|
||||
| 0x44 (68) | Pan motor B2 |
|
||||
|
||||
### Mods
|
||||
#### USB Serial port
|
||||
|
|
@ -121,7 +121,7 @@ If you find it hard to solder the wires on the camera micro usb connector get a
|
|||
The camera uBoot is password protected with "pps_password".
|
||||
|
||||
### Creating a backup
|
||||
To backup the original firmware you need a usb serial adapter connected to the board and a sdcard.
|
||||
To back up the original firmware you need a USB serial adapter connected to the board and a sdcard.
|
||||
|
||||
Find out your flash chip size:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -131,7 +131,7 @@ D:0x20 0x70 0x17
|
|||
Name:"XM25QH64AHIG"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
uBoot commands to backup the entire flash memory on the sdcard (**all sdcard contents will be lost**).
|
||||
uBoot commands to back up the entire flash memory on the sdcard (**all sdcard contents will be lost**).
|
||||
Depending on your camera flash memory size replace \<size1\>/\<size2\> with:
|
||||
- 0x800000/0x4000 for 8M flash
|
||||
- 0x1000000/0x8000 for a 16Mb flash
|
||||
|
|
@ -160,7 +160,7 @@ pps #
|
|||
|
||||
This will write the entire flash to the mmc card in "raw mode" (no filesystem).
|
||||
|
||||
**WARNING**: if you leave the card inserted in the camera and it boots the original FW, the card will be formated and the backup lost!
|
||||
**WARNING**: if you leave the card inserted in the camera, and it boots the original FW, the card will be formated and the backup lost!
|
||||
|
||||
Then to save the dump to a file, insert the card in a system running linux and:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -429,7 +429,7 @@ Content-Length: 129
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In the latest FW they have removed the "telnetd" binary so you need to place it on the sdcard:
|
||||
In the latest FW they have removed the "telnetd" binary, so you need to place it on the sdcard:
|
||||
[telnetd.zip](https://github.com/ljalves/wiki/files/7875319/telnetd.zip)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -775,23 +775,22 @@ nightMode:
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### LEDs
|
||||
The camera has a dual color led (red/blue) connected to gpio's 50 and 51.
|
||||
To control those leds you can use the /sys api:
|
||||
The camera has a dual color LED (red/blue) connected to GPIO's 50 and 51.
|
||||
To control those LEDs you can use the /sys api:
|
||||
```
|
||||
# make the gpios accessible
|
||||
# make the GPIOs accessible
|
||||
echo 50 > /sys/class/gpio/export
|
||||
# and set direction (only need to do once)
|
||||
echo out > /sys/class/gpio50/direction
|
||||
echo out > /sys/class/gpio51/direction
|
||||
|
||||
# turn on blue led
|
||||
# turn on blue LED
|
||||
echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio50/value
|
||||
# turn off blue led
|
||||
# turn off blue LED
|
||||
echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio50/value
|
||||
|
||||
# turn on red led
|
||||
# turn on red LED
|
||||
echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio51/value
|
||||
# turn off red led
|
||||
# turn off red LED
|
||||
echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio51/value
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Run ipctool
|
||||
-----------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
GPIO Settings
|
||||
-------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Supported devices
|
||||
-----------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Help: U-boot
|
||||
------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,13 +1,13 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Help: Web UI
|
||||
------------
|
||||
|
||||
### Updating Web UI from Web UI
|
||||
|
||||
In some cases, especially if you think something does not work as it should, try
|
||||
to update Web UI once again, overriding version checking for the second update.
|
||||
This may be required because we've made some changes to the updating routine,
|
||||
thus you need to update the routine code with the first update, and then to use
|
||||
the updated code during the second round of updating.
|
||||
In some cases, especially if you think that something does not work as it should,
|
||||
try to update Web UI once more, overriding version checking for the second update.
|
||||
This may be required because of some changes we have possibly made to the updating
|
||||
routine, thus you shall retrieve the updating routine code with the first update,
|
||||
and then use it for the consecutive update.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Overview
|
||||
--------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
75
en/index.md
75
en/index.md
|
|
@ -1,75 +0,0 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## Introduction
|
||||
- [About the project](menu-index.md)
|
||||
- [Supported devices](guide-supported-devices.md)
|
||||
- [Changelog](show-changelog.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## Subprojects
|
||||
- [coupler](https://openipc.org/coupler)
|
||||
- [firmware](https://openipc.org/firmware)
|
||||
- [ipctool](https://openipc.org/ipctool)
|
||||
- [telemetry](https://openipc.org/telemetry)
|
||||
- [Firmware Partitions Calculation](https://themactep.com/tools/firmware-partitions-calculation)
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
- [Installation on Goke based boards](install-goke.md)
|
||||
- [Installation on HiSilicon based boards](install-hisi.md)
|
||||
- [Installation on Novatek based boards](install-novatek.md)
|
||||
- [Installation on SigmaStar based boards](install-ssc335.md)
|
||||
- [Installation on XM510 based boards](install-xm510.md)
|
||||
- [Installation on XM530 based boards](install-xm530.md)
|
||||
- [Very old full manual](old-manual.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
- [System features](system-features.md)
|
||||
- [Majestic streamer](majestic-streamer.md)
|
||||
- [Microbe web interface](microbe-web.md)
|
||||
- [Upgrade firmware](sysupgrade.md)
|
||||
- [Image quality tuning](image-quality-tuning.md)
|
||||
- [Memory tuning](memory-tuning.md)
|
||||
- [Using ipctool](example-ipctool.md)
|
||||
- [GPIO settings](gpio-settings.md)
|
||||
- [ACMEv2](acme-v2.md)
|
||||
- [YouTube streaming](youtube-streaming.md)
|
||||
- [WiFi XM530](wifi-xm530.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## Firmware
|
||||
- [Releases in GitHub](https://github.com/OpenIPC/firmware/releases/tag/latest)
|
||||
- [Releases in Telegram](https://t.me/s/openipc_dev)
|
||||
- [Source code](source-code.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## Development
|
||||
- [Interesting tricks](dev-tricks.md)
|
||||
- [Boot device with NFS](dev-nfs-boot.md)
|
||||
- [FFMPEG usage](dev-ffmpeg-usage.md)
|
||||
- [Kernel configuration for adding new platforms](integration-kernel.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## Help, Tips, and Tricks
|
||||
- [U-boot](help-uboot.md)
|
||||
- [Web UI](help-webui.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## Reference Book
|
||||
- [Board manufacturers](board-manufacturers.md)
|
||||
- [Company names](company-names.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## Contacts
|
||||
- [Bug reports](https://github.com/OpenIPC/firmware/issues)
|
||||
|
||||
## Our resources
|
||||
- [OpenIPC](https://openipc.org/)
|
||||
- [OpenCollective](https://opencollective.com/openipc)
|
||||
- [Twitter](https://twitter.com/OpenIPC)
|
||||
- [Telegram](https://t.me/openipc)
|
||||
|
||||
## Roadmap
|
||||
- [ToDo](todo-all.md)
|
||||
- [Developers](developers.md)
|
||||
- [Notes from old sources](notes-for-resorting.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## Resources for recycling and integration
|
||||
- <https://github.com/OpenIPC/camerasrnd>
|
||||
- <https://openwrt.org/docs/techref/hardware/soc/soc.hisilicon.hi35xx>
|
||||
|
||||
[logo]: ../images/logo_openipc.png
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
For XM boards with SoC GK7202V300, GK7205V200, GK7205V300 ONLY!!!
|
||||
-----------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
For XM boards with Hi35{16Ev200,16Ev300,18Ev300} SoC ONLY!!!
|
||||
------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
For XM vendor boards with NT98562 and NT98566 SoC ONLY!!!
|
||||
---------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
For Anjoy/Brovotech/Gospell/Uniview boards with SSC335 Soc ONLY!!!
|
||||
------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
For XM vendor boards with XM510 SoC ONLY!!!
|
||||
-------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
For XM vendor boards with XM530/XM550 SoC ONLY !!!
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
|
@ -55,7 +55,7 @@ saveenv
|
|||
run uk; run ur; reset
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### backup device (no tftpput)
|
||||
### Backup device (no tftpput)
|
||||
|
||||
open the serial console with a logfile
|
||||
Note: dumping via Serial takes long
|
||||
|
|
@ -67,3 +67,4 @@ md.b 0x81000000 0x800000
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
use `cut -b 11-57 | xxd -r -p` to reconstruct the binary from `md.b` output
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,542 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
OpenIPC firmware installation, step by step.
|
||||
------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1. Determine the CPU chip
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
_Hisilicon Hi3518EV100 SoC marking. Relevant symbols highlighted with yellow._
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2. Download the firmware.
|
||||
|
||||
Go to <https://github.com/OpenIPC/firmware> and find your SoC in the table of
|
||||
supported hardware. Make sure there is a downloadable binary file for that SoC.
|
||||
If you are lucky and there is a pre-compiled firmware file for your processor --
|
||||
download it onto your PC.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3. Install and set up a TFTP server.
|
||||
|
||||
TFTP stands for _Trivial File Transfer Protocol_. As the name implies, it is a
|
||||
very simple protocol intended for transferring files over a local computer
|
||||
network. TFTP does not support authentication. Its code is so tiny and simple
|
||||
that TFTP-clients are widely used in thin-clients and embedded systems for
|
||||
retrieving bootable images from a designated boot server on the local network.
|
||||
|
||||
#### If you have Linux...
|
||||
|
||||
...then it's easy. Pre-compiled and ready-to-use binary package for your distro
|
||||
most likely already exists in distro's repo, and you only need to install it and
|
||||
set it up.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo apt install tftpd-hpa
|
||||
sudo sed -i '/^TFTP_OPTIONS/s/"$/ --create"/' /etc/default/tftpd-hpa
|
||||
sudo systemctl restart tftpd-hpa.service
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you've got your own TFTP server serving files from `/srv/tftp` directory.
|
||||
Extract files from the bundle you downloaded in step two into that directly.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo tar -C /srv/tftp/ -xvf openipc.*.tgz
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 4. Connect to UART port of your camera.
|
||||
|
||||
In order to make a connection to UART port you will need a
|
||||
[serial port adapter][FTDI] for your PC.
|
||||
|
||||
__Before you connect that adapter to you camera, make sure that it's working
|
||||
voltage is set to 3.3 volt!__
|
||||
Sometimes, you only need to flip a jumper to achieve that. But in some cases you
|
||||
might need to solder a wire, a zero Ohm resistor, or make a connection between
|
||||
two contacts with a blob of solder. Some adapters support only 5 volt. In that
|
||||
case, you will need an additional [logic level converter][TLLC] connected
|
||||
between the adapter and UART port on your camera.
|
||||
|
||||
One of the contact pads you will need to connect you adapter to is GND (ground).
|
||||
It is easy to discover using a multimeter in continuity mode. Put one of the
|
||||
leads onto a well-known exposed ground pads. Usually, these are large open
|
||||
copper contact areas around mounting screw holes, USB port housing, SD card slot
|
||||
metallic walls. Use another lead to slightly touch control pads until you see or
|
||||
hear a notification from your multimeter that the circuit is closed. That means,
|
||||
you found the ground. Now, you need to find two more: `RX` and `TX`, both used
|
||||
for receiving and transmitting data, respectively. Start with `TX`. It transmits
|
||||
series of characters and quite easy to spot.
|
||||
|
||||
Be aware that you are looking for a contact with 3.3v potential between it and
|
||||
the ground. Test possible connection points with a multimeter and mark those
|
||||
showing 3.3 volt. This way you won't have to test everything, and you save
|
||||
yourself from hitting say a 12 volt connector intended for infrared LED array
|
||||
or whatnot.
|
||||
|
||||
Connect `GND` pin on your camera to `GND` pad of the adapter, connect USB
|
||||
connector of the adapter to a USB port on your PC, start a terminal emulator
|
||||
application and connect to your adapter. Use connection speed of 115200 bps,
|
||||
no flow control, no parity bit.
|
||||
|
||||
Then, connect `RX` pin on the adapter to a possible `TX` contact of UART port
|
||||
on your camera. Power the camera with its standard power adapter. If you had a
|
||||
lucky guess then you'll start seeing booting log in your terminal window. In
|
||||
some cases, if you see garbled text on you screen instead of booting kernel,
|
||||
you might need to change the connection speed to 57600 bps and try again.
|
||||
|
||||
If your screen remains blank, try another UART contact, and then another, until
|
||||
you hit the proper one.
|
||||
|
||||
After you found the `TX` pad, connect it to `RX` pin on your adapter. Yes, it is
|
||||
a cross-connection. Whatever transmits goes into a receiver and vice-versa. Now,
|
||||
put a heavy object -- a railroad nut, an antique tin solder, a shot of vodka
|
||||
(full) -- on any letter key of your computer keyboard and start connect
|
||||
remaining `TX` pin of your adapter to different pads on the camera until you see
|
||||
it backfeeding to the terminal. As it happens, you have successfully completed
|
||||
a UART connection to you camera. Now you may drink the vodka.
|
||||
|
||||
NB! Usually, there is a fourth contact on a UART connector marked `VCC`. It is
|
||||
used for powering camera during initial programming by manufacturer. We strongly
|
||||
advise not to power your camera though that pin, but use the OEM power connector
|
||||
for this purpose.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 5. Get access to the bootloader.
|
||||
|
||||
Reboot the camera and try to interrupt its boot sequence in order to access
|
||||
bootloader console by pressing a key combination on your computer keyboard,
|
||||
between the time the bootloader starts and before Linux kernel kicks in.
|
||||
Key combinations differ from vendor to vendor but, in most cases, it is
|
||||
`Ctrl-C`, less commonly -- `Enter`, `Esc` or just any key. Carefully read text
|
||||
appearing on screen while booting, you might see a hint there. Some cameras
|
||||
require more exotic combinations not revealed in booting logs. You may try to
|
||||
look them up on the internet, or ask on [our Telegram channel][telegram].
|
||||
Chances are, we have already dealt with such a camera and know the combo.
|
||||
|
||||
If you succeeded and got a command prompt then congrats, you've got access to
|
||||
your camera's bootloader.
|
||||
|
||||
From this point on, we strongly advise you to keep a record of everything you do.
|
||||
Enable session logging in your terminal. Even better, create a text file on your
|
||||
computer and write down all commands you run and how system responses to them.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 6. Save the original firmware.
|
||||
|
||||
After you get access to the bootloader console, run `help` to get a list of
|
||||
available commands. Check if you have `tftp` among them. If you do, then saving
|
||||
the original firmware should be a breeze. You only need to set up access to your
|
||||
TFTP server from step 3.
|
||||
|
||||
NB! If your bootloader does not have `tftp`, you can still make a copy of the
|
||||
original firmware. [Read here for more](help-uboot.md).
|
||||
|
||||
Check the system environment using `printenv` command. Look for `ipaddr`,
|
||||
`netmask`, `gatewayip` and `serverip` parameters. The first three set IP address,
|
||||
netmask of your camera, and the IP address of the network gateway for accessing
|
||||
local network. The fourth parameter is an IP address of your TFTP server. Assign
|
||||
the values by `setenv` command (use IP addresses and netmask corresponding to
|
||||
your local network), then save the new values into environment with `saveenv`
|
||||
command.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
setenv ipaddr 192.168.1.253
|
||||
setenv netmask 255.255.255.0
|
||||
setenv gatewayip 192.168.1.1
|
||||
setenv serverip 192.168.1.254
|
||||
saveenv
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Most IP cameras nowadays are equipped with 8 or 16 MB NOR or NAND flash memory.
|
||||
You can check the type and size of the chip installed on of your camera in the
|
||||
bootloader log output. You'll see something like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
U-Boot 2010.06-svn (Oct 21 2016 - 11:21:29)
|
||||
|
||||
Check Flash Memory Controller v100 ... Found
|
||||
SPI Nor(cs 0) ID: 0xс2 0x20 0x18
|
||||
spi_general_qe_enable(294): Error: Disable Quad failed! reg: 0x2
|
||||
Block:64KB Chip:16MB Name:"MX25L128XX"
|
||||
SPI Nor total size: 16MB
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To dump the original firmware, you need to save the contents of camera's flash
|
||||
memory to a file. For that, you must first load the contents into RAM. Here's
|
||||
how you do that. Initialize the Flash memory. Clean a region of RAM of 0x1000000
|
||||
bytes long starting from address 0x82000000*. Read contents of the Flash from
|
||||
address 0x0 0x1000000 bytes long and place it into the prepared region or RAM.
|
||||
Now, you only have to export it to a file on the TFTP server.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sf probe 0
|
||||
mw.b 0x82000000 ff 0x1000000
|
||||
sf read 0x82000000 0x0 0x1000000
|
||||
tftp 0x82000000 firmware-full.bin 0x1000000
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
NB! Please note, that the starting address and length will be different for
|
||||
different cameras with different Flash memory chips. Consult data sheets or
|
||||
seek help on [our Telegram channel][telegram].
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 7. Install OpenIPC firmware.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Part one.
|
||||
|
||||
No two camera models are alike. Different camera models consist of different
|
||||
sets of components. The most important of them, the central processor and the
|
||||
image sensor, directly affect the image quality and the range of functions
|
||||
inherent in a particular camera. Unlike desktop computer CPU, camera's processor
|
||||
handles so many functions that it got a specific name -- System-on-Chip or SoC,
|
||||
for short.
|
||||
|
||||
But even seemingly less significant components can set limitations on the camera
|
||||
and its firmware capabilities. For example, different cameras may have different
|
||||
flash memory chips installed. Some cameras may have 8MB of flash memory, while
|
||||
others may have 16MB or more. More flash memory can fit more software code and
|
||||
allow the camera to run additional services that are not available on cameras
|
||||
with less flash memory. So we decided to build two versions of our firmware:
|
||||
the basic version (_Lite_) for cameras with 8 MB of flash memory and the
|
||||
advanced version (_Ultimate_) with additional features for cameras with 16 MB
|
||||
flash memory.
|
||||
|
||||
As said before, firmware installation routine differs for different cameras.
|
||||
There are different memory addresses and different environment parameters,
|
||||
so before proceeding, determine what kind of SoC is in your camera, what sensor,
|
||||
what flash memory chip and what amount of memory is has.
|
||||
|
||||
Below we describe the procedure for installing the OpenIPC Lite firmware on a
|
||||
camera with 8 MB of flash memory, as an example. Even if your camera has larger
|
||||
flash memory, do not skip this text. Read it carefully to understand the
|
||||
principle and the sequence of operations. We will provide specific commands
|
||||
for different cameras in the second part of this section.
|
||||
|
||||
##### Preparation.
|
||||
|
||||
So, we have a guinea pig, a camera with hi3518ev100 SoC, equipped with a OV9712
|
||||
sensor and 64 MB of RAM.
|
||||
|
||||
Connect to the camera via the UART port and access the bootloader console.
|
||||
Set the component parameters to the appropriate environment variables:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
setenv soc hi3518ev100
|
||||
setenv sensor ov9712
|
||||
setenv totalmem 64M
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Set environment variables for loading the Linux kernel and the root file system
|
||||
of the new firmware:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
setenv osmem 32M
|
||||
setenv bootargs 'mem=${osmem:-32M} console=ttyAMA0,115200 panic=20 root=/dev/mtdblock3 rootfstype=squashfs init=/init mtdparts=hi_sfc:256k(boot),64k(env),2048k(kernel),5120k(rootfs),-(rootfs_data)'
|
||||
setenv bootcmd 'setenv setargs setenv bootargs ${bootargs}; run setargs; sf probe 0; sf read 0x82000000 0x50000 0x200000; bootm 0x82000000'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Set environment variables for the camera to access local network, where
|
||||
`ethaddr` is the original camera MAC address, `ipaddr` is camera's IP address
|
||||
on the network, `gatewayip` is the IP address of a router to access the network,
|
||||
`netmask` is the subnet mask, and `serverip` is am IP address of the TFTP server
|
||||
from step 3.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
setenv ethaddr 00:12:16:00:00:00
|
||||
setenv ipaddr 192.168.1.10
|
||||
setenv netmask 255.255.255.0
|
||||
setenv gatewayip 192.168.1.1
|
||||
setenv serverip 192.168.1.254
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Save updated values to flash memory.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
saveenv
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### Installation.
|
||||
|
||||
First, clear the memory region at address 0x82000000, 0x1000000 bytes long, by
|
||||
writing 0xff to it. Then retrieve kernel file for the camera from the TFTP
|
||||
server and place it into memory starting with address 0x82000000.
|
||||
|
||||
The `$soc` variable in the name of the requested file is substituted with its
|
||||
value from the environment variables created earlier. In this example, the file
|
||||
named `uImage.hi3518ev100` will be requested from the server.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mw.b 0x82000000 ff 1000000
|
||||
tftp 0x82000000 uImage.${soc}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
NB! Pay attention to the messages on the terminal screen! If any of the commands
|
||||
throws an error, find out what went wrong. Maybe you made a typo? In any case,
|
||||
do not continue the procedure until all previous commands succeed. Otherwise,
|
||||
you might end up with a bricked camera!
|
||||
|
||||
So, you've made sure that the file is downloaded and placed in the camera's RAM.
|
||||
Now you need to write it down to the flash memory. To do that, you need to get
|
||||
access to the flash memory, then clean erase the region from address 0x50000
|
||||
that is 0x200000 bytes long, and copy the contents of camera's RAM from address
|
||||
0x82000000 and the size of the kernel file to the flash memory starting at
|
||||
address 0x50000.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sf probe 0
|
||||
sf erase 0x50000 0x200000
|
||||
sf write 0x82000000 0x50000 ${filesize}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, you need to repeat the process for the root file system, saving it to the
|
||||
next region starting from address 0x250000 of 0x500000 bytes long.
|
||||
|
||||
NB! 0x500000 bytes is a hexadecimal equivalent of 5242880 bytes in decimal
|
||||
system, and equals 5120 kilobytes, exactly what we have prepared for rootfs
|
||||
in `bootargs` parameter.
|
||||
|
||||
It is easy to memorize the sequence if you give it a little thought:
|
||||
clean RAM, download file there, unlock flash chip, wipe the target region in
|
||||
flash memory, write file from memory into there.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mw.b 0x82000000 ff 1000000
|
||||
tftp 0x82000000 rootfs.squashfs.${soc}
|
||||
sf probe 0
|
||||
sf erase 0x250000 0x500000
|
||||
sf write 0x82000000 0x250000 ${filesize}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After both partitions have been successfully written to the flash memory and all
|
||||
necessary changes have been made to the bootloader to prepare it for starting
|
||||
the new firmware, it is time to reboot the camera. To do that, type this command
|
||||
in the console:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
reset
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Part two.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have read the first part of this section (if not - go read it), then you
|
||||
already know what manipulations and why you need to do to install the OpenIPC
|
||||
firmware. And all you need are the commands suitable for your particular camera.
|
||||
|
||||
Below are samples of such commands for cameras equipped with [Goke](#goke),
|
||||
[HiSilicon](#hisilicon), [SigmaStar/MStar](#sigmastarmstar), [XM](#xm) SoCs.
|
||||
|
||||
##### Goke
|
||||
|
||||
SoC: gk7202v300, gk7205v200, gk7205v300
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
setenv soc <processor> # gk7202v300, gk7205v200, or gk7205v300.
|
||||
setenv sensor <sensor> #
|
||||
setenv totalmem <memory> # 64M for gk7202v300, gk7205v200, 128M for gk7205v300.
|
||||
|
||||
setenv osmem 32M
|
||||
setenv bootargs 'mem=${osmem:-32M} console=ttyAMA0,115200 panic=20 root=/dev/mtdblock3 rootfstype=squashfs init=/init mtdparts=sfc:256k(boot),64k(env),2048k(kernel),5120k(rootfs),-(rootfs_data)'
|
||||
setenv bootcmd 'setenv setargs setenv bootargs ${bootargs}; run setargs; sf probe 0; sf read 0x42000000 0x50000 0x200000; bootm 0x42000000'
|
||||
|
||||
setenv ethaddr 00:00:00:00:00:00
|
||||
setenv ipaddr 192.168.1.10
|
||||
setenv netmask 255.255.255.0
|
||||
setenv gatewayip 192.168.1.1
|
||||
setenv serverip 192.168.1.254
|
||||
|
||||
saveenv
|
||||
|
||||
mw.b 0x42000000 ff 1000000
|
||||
tftp 0x42000000 uImage.${soc}
|
||||
sf probe 0
|
||||
sf erase 0x50000 0x200000
|
||||
sf write 0x42000000 0x50000 ${filesize}
|
||||
|
||||
mw.b 0x42000000 ff 1000000
|
||||
tftp 0x42000000 rootfs.squashfs.${soc}
|
||||
sf probe 0
|
||||
sf erase 0x250000 0x500000
|
||||
sf write 0x42000000 0x250000 ${filesize}
|
||||
|
||||
reset
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### HiSilicon
|
||||
|
||||
SoC: hi3516ev200, hi3516ev300, hi3518ev300.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
setenv soc <processor> # hi3516ev200, hi3516ev300, or hi3518ev300.
|
||||
setenv sensor <sensor> #
|
||||
setenv totalmem <memory> # 64M for hi3516ev200, hi3518ev300, 128M for hi3516ev300.
|
||||
|
||||
setenv osmem 32M
|
||||
setenv bootargs 'mem=${osmem:-32M} console=ttyAMA0,115200 panic=20 root=/dev/mtdblock3 rootfstype=squashfs init=/init mtdparts=hi_sfc:256k(boot),64k(env),2048k(kernel),5120k(rootfs),-(rootfs_data)'
|
||||
setenv bootcmd 'setenv setargs setenv bootargs ${bootargs}; run setargs; sf probe 0; sf read 0x42000000 0x50000 0x200000; bootm 0x42000000'
|
||||
|
||||
setenv ethaddr 00:00:00:00:00:00
|
||||
setenv ipaddr 192.168.1.10
|
||||
setenv netmask 255.255.255.0
|
||||
setenv gatewayip 192.168.1.1
|
||||
setenv serverip 192.168.1.254
|
||||
|
||||
saveenv
|
||||
|
||||
mw.b 0x42000000 ff 1000000
|
||||
tftp 0x42000000 uImage.${soc}
|
||||
sf probe 0
|
||||
sf erase 0x50000 0x200000
|
||||
sf write 0x42000000 0x50000 ${filesize}
|
||||
|
||||
mw.b 0x42000000 ff 1000000
|
||||
tftp 0x42000000 rootfs.squashfs.${soc}
|
||||
sf probe 0
|
||||
sf erase 0x250000 0x500000
|
||||
sf write 0x42000000 0x250000 ${filesize}
|
||||
|
||||
reset
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### SigmaStar/MStar
|
||||
|
||||
SoC: ssc325, ssc335, ssc337.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
setenv soc <processor> # ssc325, ssc335, or ssc337.
|
||||
setenv sensor <sensor> # gc2053, imx307, or sc3335.
|
||||
setenv totalmem 64M
|
||||
|
||||
setenv osmem 32M
|
||||
setenv bootargs 'mem=${osmem:-32M} console=ttyS0,115200 panic=20 root=/dev/mtdblock3 rootfstype=squashfs init=/init LX_MEM=0x3fe0000 mma_heap=mma_heap_name0,miu=0,sz=0x1C00000 mma_memblock_remove=1 mtdparts=NOR_FLASH:256k(boot),64k(tech),2048k(kernel),5120k(rootfs),-(rootfs_data)'
|
||||
setenv bootcmd 'setenv setargs setenv bootargs ${bootargs}; run setargs; sf probe 0; sf read 0x21000000 0x50000 0x200000; bootm 0x21000000'
|
||||
|
||||
setenv ethaddr 00:00:00:00:00:00
|
||||
setenv ipaddr 192.168.1.10
|
||||
setenv netmask 255.255.255.0
|
||||
setenv gatewayip 192.168.1.1
|
||||
setenv serverip 192.168.1.254
|
||||
|
||||
saveenv
|
||||
|
||||
mw.b 0x21000000 ff 1000000
|
||||
tftpboot 0x21000000 uImage.${soc}
|
||||
sf probe 0
|
||||
sf erase 0x50000 0x200000
|
||||
sf write 0x21000000 0x50000 ${filesize}
|
||||
|
||||
mw.b 0x21000000 ff 1000000
|
||||
tftpboot 0x21000000 rootfs.squashfs.${soc}
|
||||
sf probe 0
|
||||
sf erase 0x250000 0x500000
|
||||
sf write 0x21000000 0x250000 ${filesize}
|
||||
|
||||
reset
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### XM
|
||||
|
||||
SoC: xm510, xm530, xm550.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
setenv soc <processor> # xm510 for xm510, xm530 for both xm530 and xm550.
|
||||
setenv sensor <sensor> #
|
||||
setenv totalmem <memory> # 32M for xm510, 64M for xm530, 128M for xm550.
|
||||
|
||||
setenv osmem <osmemory> # 18M for xm510, 35M for xm530, 64M for xm550.
|
||||
setenv bootargs 'mem=35M console=ttyAMA0,115200 panic=20 root=/dev/mtdblock3 rootfstype=squashfs init=/init mtdparts=xm_sfc:256k(boot),64k(env),2048k(kernel),5120k(rootfs),-(rootfs_data)'
|
||||
setenv bootcmd 'sf probe 0; sf read 0x80007fc0 0x50000 0x200000; bootm 0x80007fc0'
|
||||
|
||||
setenv ethaddr 00:00:00:00:00:00
|
||||
setenv ipaddr 192.168.1.10
|
||||
setenv netmask 255.255.255.0
|
||||
setenv gatewayip 192.168.1.1
|
||||
setenv serverip 192.168.1.254
|
||||
|
||||
saveenv
|
||||
|
||||
mw.b 0x80007fc0 ff 1000000
|
||||
tftp 0x80007fc0 uImage.${soc}
|
||||
sf probe 0
|
||||
sf erase 0x50000 0x200000
|
||||
sf write 0x80007fc0 0x50000 ${filesize}
|
||||
|
||||
mw.b 0x80007fc0 ff 1000000
|
||||
tftp 0x80007fc0 rootfs.squashfs.${soc}
|
||||
sf probe 0
|
||||
sf erase 0x250000 0x500000
|
||||
sf write 0x80007fc0 0x250000 ${filesize}
|
||||
|
||||
reset
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 8. First boot.
|
||||
|
||||
If all previous steps are done correctly, your camera should start with the new
|
||||
firmware. Welcome to OpenIPC!
|
||||
|
||||
After the first boot with the new firmware you need to clean the overlay
|
||||
partition. Run this in your terminal window:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
firstboot
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Step aside.
|
||||
|
||||
To facilitate subsequent firmware upgrades directly from the bootloader console,
|
||||
create two macros with sequences of commands needed to boot from the TFTP server
|
||||
and write kernel and root file system for your camera model into flash memory.
|
||||
|
||||
We will use `uk` and `ur` for macro names, which can be decoded as `update kernel`
|
||||
and `update rootfs`. Easy to remember.
|
||||
|
||||
As you remember, in the example above we used the following commands to install the kernel:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mw.b 0x42000000 ff 1000000
|
||||
tftp 0x42000000 uImage.${soc}
|
||||
sf probe 0
|
||||
sf erase 0x50000 0x200000
|
||||
sf write 0x42000000 0x50000 ${filesize}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To create the `uk` macro, join all the above commands into one line, alternating
|
||||
them with semicolons. For added protection against writing invalid data to flash
|
||||
memory in case file downloading from TFTP server fails, replace semicolon before
|
||||
`sf probe 0` with logical AND operator (`&&`). It will make macro to abort if
|
||||
file fails to download.
|
||||
```
|
||||
fw_setenv uk 'mw.b 0x42000000 ff 1000000; tftp 0x42000000 uImage.${soc} && sf probe 0; sf erase 0x50000 0x200000; sf write 0x42000000 0x50000 ${filesize}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Do the same with the root file system commands:
|
||||
```
|
||||
mw.b 0x82000000 ff 1000000
|
||||
tftp 0x82000000 rootfs.squashfs.${soc}
|
||||
sf probe 0
|
||||
sf erase 0x250000 0x500000
|
||||
sf write 0x82000000 0x250000 ${filesize}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
saving result as `ur` macro:
|
||||
```
|
||||
fw_setenv ur 'mw.b 0x42000000 ff 1000000; tftp 0x42000000 rootfs.squashfs.${soc} && sf probe 0; sf erase 0x250000 0x500000; sf write 0x42000000 0x250000 ${filesize}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Naturally, to create your own macro, you should use the commands suitable for
|
||||
your specific camera, not mindlessly copying the above lines, but using them as
|
||||
an example and understanding the actions to be taken.
|
||||
|
||||
NB! Although these commands create a macro to run in the bootloader console,
|
||||
they must be executed inside Linux environment. This way we avoid the
|
||||
restrictions on the number of arguments in the `setenv` command existing in
|
||||
some older versions of the bootloader.
|
||||
|
||||
You will now be able to flash both kernel and root file system followed by
|
||||
rebooting the camera directly from the bootloader console. It's as easy as that!
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
run uk; run ur; reset
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[logo]: ../images/logo_openipc.png
|
||||
[FTDI]: https://www.google.com/search?q=ftdi+usb+ttl
|
||||
[TLLC]: https://google.com/search?q=logic+level+converter+3.3v+5v
|
||||
[telegram]: https://t.me/OpenIPC
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Additional requirements for kernel configuration
|
||||
------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
|
@ -27,4 +27,4 @@ Patch files should be named `<number>-<description>.patch`.
|
|||
- The field `<number>` in the patch file name refers to the apply order, and shall start at 1.
|
||||
It is preferred to pad the number with zeros up to 4 digits, like git-format-patch does. E.g.: _0001-foobar-the-buz.patch_
|
||||
- A message explaining what the patch does, and why it is needed, should be added in the header commentary of the patch.
|
||||
- You should add a Signed-off-by statement in the header of the each patch to help with keeping track of the changes and to certify that the patch is released under the same license as the software that is modified.
|
||||
- You should add a Signed-off-by statement in the header of each patch to help with keeping track of the changes and to certify that the patch is released under the same license as the software that is modified.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Majestic Streamer
|
||||
-----------------
|
||||
|
|
@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ With firmware running, you can access the camera using URLs below
|
|||
and others are image width and height.
|
||||
* http://192.168.1.10/image.heif - image snapshot in [HEIF][heif] format,
|
||||
use `stream` parameter to specify channel (the same approach as for RTSP channels)
|
||||
* http://192.168.1.10/image.yuv - image snapshot in [YUV420][yuv] format.
|
||||
* http://192.168.1.10/image.yuv420 - image snapshot in [YUV420][yuv] format.
|
||||
* http://192.168.1.10/image.dng - [raw image][raw] snapshot from the sensor in
|
||||
[Adobe DNG][dng] format (only for v>=2 HiSilicon processors).
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -50,7 +50,7 @@ convert -verbose -sampling-factor 4:2:0 -size 1920x1080 -depth 8 image.yuv image
|
|||
where `1920x1080` is the picture resolution of video0, and `.png` is the target
|
||||
image format.
|
||||
|
||||
### Audio input
|
||||
### Audio
|
||||
|
||||
* http://192.168.1.10/audio.opus - [Opus][opus] audio stream.
|
||||
* http://192.168.1.10/audio.m4a - [AAC][aac] audio stream.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
HiSilicon boards
|
||||
----------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,2 +1,2 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## Basic information
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -111,7 +111,7 @@ You can make a financial contribution to the project at [Open Collective](https:
|
|||
|
||||
Thank you.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<p style="text-align:center">
|
||||
<a href="https://opencollective.com/openipc/contribute/backer-14335/checkout" target="_blank"><img src="https://opencollective.com/webpack/donate/button@2x.png?color=blue" width="375" alt="Open Collective donate button"></a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,7 +1,19 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Microbe web interface
|
||||
---------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Default login/password: admin/12345
|
||||
Web Interface is available on port 85 as _http://camera-ip:85_.
|
||||
Default login and password are _admin_ and _12345_, respectively.
|
||||
|
||||
### Updating the web interface from the web interface
|
||||
|
||||
In some cases, especially if it seems that something is not working, you might
|
||||
need to re-install the web interface update by checking the "Install even if
|
||||
matches the existing version." checkbox.
|
||||
|
||||
Double updating of the web interface can be necessary if we've made some changes
|
||||
to the code of updating procedure per se. In such case, the first update routine
|
||||
will install the modified code, and the second round will be performed using
|
||||
that updated code.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Installation: how to make OpenIPC running on certain hardware
|
||||
-------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
|
@ -16,7 +16,8 @@ Here are some examples:
|
|||
|
||||
## How to upgrade OpenIPC
|
||||
|
||||
Currently full automatic system upgrade like [sysupgrade](https://github.com/openwrt/openwrt/blob/master/package/base-files/files/sbin/sysupgrade) in OpenWRT is not supported. Use partial manual update instead.
|
||||
Currently, full automatic system upgrade like [sysupgrade][openwrtsysupgrade]
|
||||
in OpenWRT is not supported. Use partial manual update instead.
|
||||
|
||||
### Partial manual update
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -28,15 +29,20 @@ The process is described on the main site on [firmware page](https://openipc.org
|
|||
|
||||
* Can OpenIPC be installed on Raspberry Pi or other hardware?
|
||||
|
||||
No. Currently only HiSilicon HI35xx SoC are supported. But theoretically it is possible to support other architectures and boards. Though it will require a lot of efforts and thus it is not a near time focus of the project.
|
||||
No. Currently, only HiSilicon HI35xx SoC are supported. But theoretically it is
|
||||
possible to support other architectures and boards. Though it will require a lot
|
||||
of efforts, and thus it is not a near time focus of the project.
|
||||
|
||||
* Can I flash OpenIPC image without using UART console and TFTP?
|
||||
|
||||
No. Currently it is not possible, though we are working on this.
|
||||
No. Currently, it is not possible, though we are working on this.
|
||||
|
||||
* What the difference between OpenIPC based on BuildRoot and based on OpenWRT?
|
||||
|
||||
Buildroot is faster for initial development for new platforms as it is minimalistic and has no dependencies. OpenWRT is convenient for users as a final product, but there are a lot of complexities, dependencies, and there is no point in developing without a community.
|
||||
Buildroot is faster for initial development for new platforms as it is
|
||||
minimalistic and has no dependencies. OpenWRT is convenient for users as a final
|
||||
product, but there are a lot of complexities, dependencies, and there is no
|
||||
point in developing without a community.
|
||||
|
||||
### Other FAQs
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -45,7 +51,7 @@ Buildroot is faster for initial development for new platforms as it is minimalis
|
|||
|
||||
## Network related stuff
|
||||
|
||||
Common network configuration can be done in Luci GUI:
|
||||
Common network configuration can be done in Luci GUI:
|
||||
|
||||
`http://<your camera IP>`
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -57,32 +63,34 @@ There are two branches of OpenIPC currently:
|
|||
|
||||
### OpenWRT based
|
||||
|
||||
GUI is based on Luci. There are menu sections for camera specific setup.
|
||||
GUI is based on Luci. There are menu sections for camera specific setup.
|
||||
|
||||
### Buildroot based
|
||||
|
||||
Tere is a different interface planned... Still under development.
|
||||
There is a different interface planned... Still under development.
|
||||
|
||||
## Hardware related recommendations
|
||||
|
||||
### Power Over Internet PoE
|
||||
|
||||
It is advised to use 48V power adapters with RJ-45 connectors instead of 12V. With 12V adapters the current will be 4 times higher. High current can burn RJ-45 connectors and wires.
|
||||
It is advised to use 48V power adapters with RJ-45 connectors instead of 12V.
|
||||
With 12V adapters the current will be 4 times higher. High current can burn
|
||||
RJ-45 connectors and wires.
|
||||
|
||||
## How to stream video to Internet
|
||||
|
||||
* [[MiniHttp]] ➤ main audio/video streamer of the OpenIPC based system
|
||||
* __MiniHttp__ ➤ main audio/video streamer of the OpenIPC based system.
|
||||
|
||||
* [[Мajestic]] ➤ new (in development) audio/video streamer of the OpenIPC based system
|
||||
* __Мajestic__ ➤ new (in development) audio/video streamer of the OpenIPC based system.
|
||||
|
||||
* [[YouTube Sreaming]]
|
||||
* __YouTube Streaming__
|
||||
|
||||
#### MiniHttp is the main streamer of the OpenIPC based system
|
||||
|
||||
It is important to tune configuration of MiniHttp by turning off unneeded protocols and features for better security and performance.
|
||||
It is important to tune configuration of MiniHttp by turning off unneeded
|
||||
protocols and features for better security and performance.
|
||||
|
||||
Config file is located in
|
||||
`/etc/minihttp.ini`
|
||||
Config file is located in `/etc/minihttp.ini`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Debug mode:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -97,17 +105,19 @@ Config file is located in
|
|||
|
||||
[Tools repository](https://github.com/OpenIPC/packages/tree/main/utils)
|
||||
|
||||
[ipctool](https://github.com/OpenIPC/ipctool) - gets information about hardware and outputs it in common format. Can also be used to make backup and restore of the camera software (still experimental feature).
|
||||
[ipctool](https://github.com/OpenIPC/ipctool) - gets information about hardware
|
||||
and outputs it in common format. Can also be used to make backup and restore of
|
||||
the camera software (still experimental feature).
|
||||
|
||||
## Integration examples with Digital Video Recording systems
|
||||
|
||||
[[Recording stream locally]] with various utilities.
|
||||
Recording stream locally with various utilities.
|
||||
|
||||
[[YouTube as DVR]] hack
|
||||
YouTube as DVR hack.
|
||||
|
||||
## Tips and trick on monitoring OpenIPC system
|
||||
## Tips and tricks on monitoring OpenIPC system
|
||||
|
||||
### How to get temperature from chip's internal sensor (not all devices supported):
|
||||
### How to get temperature from chip's internal sensor (where supported):
|
||||
|
||||
`ipctool --temp`
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -120,33 +130,35 @@ other commands to [[monitor temperature]]
|
|||
[[prometheus-node]]
|
||||
|
||||
### Monitoring templates
|
||||
|
||||
* [[Zabbix monitoring templates]]
|
||||
|
||||
## Prometheus node configuration
|
||||
|
||||
[Prometheus](https://prometheus.io/) is an open-source systems monitoring and alerting toolkit.
|
||||
[Prometheus](https://prometheus.io/) is an open-source systems monitoring and
|
||||
alerting toolkit.
|
||||
|
||||
OpenIPC has prometheus node exporter as a package. The result output can be viewed as a plaintext:
|
||||
|
||||
http://192.168.1.10:9100/metrics
|
||||
OpenIPC has prometheus node exporter as a package. The result output can be
|
||||
viewed as plain text on http://192.168.1.10:9100/metrics
|
||||
|
||||
Or visualized if you install [proemetheus server and graphana](https://prometheus.io/docs/visualization/grafana/):
|
||||
|
||||
[[images/preometheus_node_graphana_example.jpg]]
|
||||
|
||||
You can configure the node here
|
||||
|
||||
`/etc/config/prometheus-node-exporter-lua`
|
||||
You can configure the node in `/etc/config/prometheus-node-exporter-lua`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Meta package
|
||||
|
||||
https://github.com/ZigFisher/Glutinium/tree/master/prometheus-node-exporter-lua
|
||||
<https://github.com/ZigFisher/Glutinium/tree/master/prometheus-node-exporter-lua>
|
||||
|
||||
## Experiments with I2C on Hi3518EV200
|
||||
|
||||
### Setting up i2c-x via device tree
|
||||
|
||||
The standard i2c-hisilicon driver does not give an option to set pins to i2c mode if they were previously set to dts. To automatically set the required pins to i2c mode you just need to add the following code to the beginning of hi_i2c_hw_init (linux/drivers/i2c/busses/i2c-hisilicon.c)
|
||||
The standard i2c-hisilicon driver does not give an option to set pins to i2c
|
||||
mode if they were previously set to dts. To automatically set the required pins
|
||||
to i2c mode you just need to add the following code to the beginning of
|
||||
hi_i2c_hw_init (linux/drivers/i2c/busses/i2c-hisilicon.c)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#ifdef CONFIG_ARCH_HI3518EV200 // Might be the same for other hardware devices
|
||||
|
|
@ -173,7 +185,7 @@ if(pinfo->mem->start = 0x20250000 /* address i2c-2 */) {
|
|||
|
||||
### [[DevTools]]
|
||||
|
||||
### [[Docs on different IP cameras]]
|
||||
### [[Docs on different IP cameras]]
|
||||
|
||||
### Groups in Telegram related to development:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -182,7 +194,9 @@ if(pinfo->mem->start = 0x20250000 /* address i2c-2 */) {
|
|||
|
||||
## Tools used in Research and Development
|
||||
|
||||
[hisi-trace](https://github.com/OpenIPC/hisi-trace) --> tool to run Sofia inside the OpenIPC. Allows porting stock Sofia functions to the target system without loading in the original firmware.
|
||||
[hisi-trace](https://github.com/OpenIPC/hisi-trace) --> tool to run Sofia inside
|
||||
the OpenIPC. Allows porting stock Sofia functions to the target system without
|
||||
loading in the original firmware.
|
||||
|
||||
[some tools for dissassembling](https://github.com/TekuConcept/ArmElfDisassembler)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -192,7 +206,7 @@ if(pinfo->mem->start = 0x20250000 /* address i2c-2 */) {
|
|||
|
||||
Different hack & mod related to IP Cameras forums:
|
||||
|
||||
https://www.goprawn.com/
|
||||
<https://www.goprawn.com/>
|
||||
|
||||
Below are some examples how to record video streams with various utilities.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -230,7 +244,7 @@ Password: xmhdipc
|
|||
Welcome to HiLinux.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Also can try [other pairs](https://gist.github.com/gabonator/74cdd6ab4f733ff047356198c781f27d)
|
||||
Also, can try [other pairs](https://gist.github.com/gabonator/74cdd6ab4f733ff047356198c781f27d)
|
||||
|
||||
### Optional: enable Linux kernel verbose boot (where armbenv exists)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -245,6 +259,7 @@ Or in case where XmEnv exists:
|
|||
# XmEnv -s xmuart 0
|
||||
# reboot
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Enable telnet without even open your camera (remotely)
|
||||
|
||||
* Find proper zip with recent firmware update using [link](https://translate.google.com/translate?hl=en&sl=ru&tl=en&u=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.cctvsp.ru%2Farticles%2Fobnovlenie-proshivok-dlya-ip-kamer-ot-xiong-mai) and download it.
|
||||
|
|
@ -263,9 +278,10 @@ Or in case where XmEnv exists:
|
|||
* Run `./add_xmaurt.sh` and then ensure that `u-boot.env.img` has
|
||||
`xmuart=1telnetctrl=1` near the end of file.
|
||||
|
||||
* Repack `bin` file adding changed `u-boot.env.img` there like this: `zip -u General_IPC_HI3516EV200_85H30AI_S38.Nat.dss.OnvifS.HIK_V5.00.R02.20200507_all.bin u-boot.env.img`
|
||||
* Repack `bin` file adding changed `u-boot.env.img` there like this:
|
||||
`zip -u General_IPC_HI3516EV200_85H30AI_S38.Nat.dss.OnvifS.HIK_V5.00.R02.20200507_all.bin u-boot.env.img`
|
||||
|
||||
* Upgrade camera using new `bin` file
|
||||
* Upgrade camera using new `bin` file.
|
||||
|
||||
Document origin is [here](https://github.com/OpenIPC/camerasrnd/blob/master/get_telnet.md)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -323,42 +339,43 @@ fi
|
|||
|
||||
## Direct streaming to YouTube
|
||||
|
||||
YouTube offers not only LiveStreming but also can record this stream.
|
||||
YouTube offers not only LiveStreaming but also can record this stream.
|
||||
|
||||
Up to 12 hours of LiveStream can be recorded.
|
||||
Up to 12 hours of LiveStream can be recorded.
|
||||
|
||||
Direct streaming to YouTube is possible but not currently supported by OpenIPC.
|
||||
|
||||
### Direct streaming can be done with MiniHttp
|
||||
|
||||
Direct streaming to YouTube could be done with the help of RTMP but there are currently no plans add this protocol to the main streamer MiniHttp.
|
||||
Direct streaming to YouTube could be done with the help of RTMP but there are
|
||||
currently no plans add this protocol to the main streamer MiniHttp.
|
||||
|
||||
### Direct streaming can be done with FFMPEG
|
||||
|
||||
There are two modes available: "old one", H264 over RTMP an a "new one", H265 over HLS.
|
||||
There are two modes available: the old one, supporting H264 over RTMP,
|
||||
and the new one, with H265 over HLS.
|
||||
|
||||
Both methods were not tested in production and still in development mode. See following links for details:
|
||||
Both methods were not tested in production and still are in development mode.
|
||||
See following links for details:
|
||||
|
||||
### H264 over RTMP
|
||||
|
||||
Navigate to the compiled package [H264 over RTMP](https://github.com/ZigFisher/Glutinium/tree/master/hi35xx-ffmpeg/files)
|
||||
|
||||
Copy file **silence.aac** to /usr/lib/
|
||||
|
||||
and file **ffmpeg** to /usr/sbin/
|
||||
Copy file `silence.aac` to `/usr/lib/` and file `ffmpeg` to `/usr/sbin/`
|
||||
|
||||
Also set execution permission:
|
||||
|
||||
`chmod +x /usr/sbin/ffmpeg`
|
||||
|
||||
Run ffmpeg with the following parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
ffmpeg -stream_loop -1 -i /usr/lib/silence.aac -rtsp_transport udp -thread_queue_size 64 -i rtsp://127.0.0.1:554/stream=0 -c
|
||||
:v copy -c:a copy -f flv rtmp://a.rtmp.youtube.com/live2/<your key>
|
||||
Run `ffmpeg` with the following parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
`ffmpeg -stream_loop -1 -i /usr/lib/silence.aac -rtsp_transport udp -thread_queue_size 64 -i rtsp://127.0.0.1:554/stream=0 -c:v copy -c:a copy -f flv rtmp://a.rtmp.youtube.com/live2/<your key>`
|
||||
|
||||
[H265 over HLS](https://gist.github.com/widgetii/ec275524dd621cd55774c952bee4c622)
|
||||
|
||||
Some build instructions:
|
||||
|
||||
https://github.com/ZigFisher/Glutinium/blob/master/hi35xx-ffmpeg/0_Build.sh
|
||||
<https://github.com/ZigFisher/Glutinium/blob/master/hi35xx-ffmpeg/0_Build.sh>
|
||||
|
||||
[openwrtsysupgrade]: https://github.com/openwrt/openwrt/blob/master/package/base-files/files/sbin/sysupgrade
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Introduction
|
||||
------------
|
||||
|
|
@ -585,7 +585,7 @@ reboot
|
|||
|
||||
### Recover backup firmware
|
||||
|
||||
If something goes horribly wrong and you want back your backed up firmware
|
||||
If something goes horribly wrong, and you want your backed up firmware back
|
||||
|
||||
**Restore backup up firmware via serial**
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Changelog
|
||||
---------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Source code
|
||||
-----------
|
||||
|
|
@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ make BOARD=unknown_unknown_xm530_openipc all
|
|||
|
||||
## Statistical data
|
||||
|
||||
Software might do product usage data collection including SoC and sensor model name to gather statistics used in QA process..
|
||||
Software might do product usage data collection including SoC and sensor model name to gather statistics used in QA process.
|
||||
|
||||
We guaranty that the data is fully anonymized, and does not contain anything that can arguably be considered data about an individual, that could be considered end-user data; or that could be sensitive or confidential to users.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
System features
|
||||
---------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Upgrading firmware
|
||||
------------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
ToDo
|
||||
----
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
WiFi for XM530 based devices
|
||||
----------------------------
|
||||
Wi-Fi for XM530 based devices
|
||||
-----------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Save this script as `/usr/sbin/wifi`
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,11 +1,11 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Table of Content](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Configuration requirements
|
||||
--------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
To prevent accidental stream termination on temporary connection drops
|
||||
schedule live streaming with a start date in the far future (e.g. December 31st
|
||||
schedule live-streaming with a start date in the far future (e.g. December 31st
|
||||
of the current year). It will work smoothly when you go live, disconnect the
|
||||
camera and then continue streaming.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -37,7 +37,7 @@ for more information.
|
|||
deselect 'API Key' option, then press 'Execute' button below.
|
||||
- Authorize yourself using your YouTube connected account.
|
||||
- Make sure that you got 200 response otherwise check errors and repeat.
|
||||
Trivial error is when [live streaming](https://support.google.com/youtube/answer/2474026?hl=en)
|
||||
Trivial error is when [live-streaming](https://support.google.com/youtube/answer/2474026?hl=en)
|
||||
was not previously enabled in your account.
|
||||
- Save "channelId" from the response (it looks like "UCPJRjbxYlq6h2cCqy8RCRjg").
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
|
|||
OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
============
|
||||
|
||||
> "Improving the world, one patch at a time."
|
||||
|
||||
## Table of Content
|
||||
|
||||
### Introduction
|
||||
- [About the project](en/menu-index.md)
|
||||
- [Supported devices](en/guide-supported-devices.md)
|
||||
- [Changelog](en/show-changelog.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### Subprojects
|
||||
- [coupler](https://openipc.org/coupler)
|
||||
- [firmware](https://openipc.org/firmware)
|
||||
- [ipctool](https://openipc.org/ipctool)
|
||||
- [telemetry](https://openipc.org/telemetry)
|
||||
- [Firmware Partitions Calculation](https://themactep.com/tools/firmware-partitions-calculation)
|
||||
|
||||
### Installation
|
||||
- [Installation, step by step](en/installation.md)
|
||||
- [Installation on Goke based boards](en/install-goke.md)
|
||||
- [Installation on HiSilicon based boards](en/install-hisi.md)
|
||||
- [Installation on Novatek based boards](en/install-novatek.md)
|
||||
- [Installation on SigmaStar based boards](en/install-ssc335.md)
|
||||
- [Installation on XM510 based boards](en/install-xm510.md)
|
||||
- [Installation on XM530 based boards](en/install-xm530.md)
|
||||
- [Very old full manual](en/old-manual.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### Usage
|
||||
- [System features](en/system-features.md)
|
||||
- [Majestic streamer](en/majestic-streamer.md)
|
||||
- [Microbe web interface](en/microbe-web.md)
|
||||
- [Upgrade firmware](en/sysupgrade.md)
|
||||
- [Image quality tuning](en/image-quality-tuning.md)
|
||||
- [Memory tuning](en/memory-tuning.md)
|
||||
- [Using ipctool](en/example-ipctool.md)
|
||||
- [GPIO settings](en/gpio-settings.md)
|
||||
- [ACMEv2](en/acme-v2.md)
|
||||
- [YouTube streaming](en/youtube-streaming.md)
|
||||
- [WiFi XM530](en/wifi-xm530.md)
|
||||
- [Board manufacturers](en/board-manufacturers.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### Firmware
|
||||
- [Releases in GitHub](https://github.com/OpenIPC/firmware/releases/tag/latest)
|
||||
- [Releases in Telegram](https://t.me/s/openipc_dev)
|
||||
- [Source code](en/source-code.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### Development
|
||||
- [Interesting tricks](en/dev-tricks.md)
|
||||
- [Boot device with NFS](en/dev-nfs-boot.md)
|
||||
- [FFMPEG usage](en/dev-ffmpeg-usage.md)
|
||||
- [Kernel configuration for adding new platforms](en/integration-kernel.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### Help, Tips, and Tricks
|
||||
- [U-boot](en/help-uboot.md)
|
||||
- [Web UI](en/help-webui.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### Reference Book
|
||||
- [Board manufacturers](en/board-manufacturers.md)
|
||||
- [Company names](en/company-names.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### Contacts
|
||||
- [Bug reports](https://github.com/OpenIPC/firmware/issues)
|
||||
|
||||
### Our resources
|
||||
- [OpenIPC](https://openipc.org/)
|
||||
- [OpenCollective](https://opencollective.com/openipc)
|
||||
- [Twitter](https://twitter.com/OpenIPC)
|
||||
- [Telegram](https://t.me/openipc)
|
||||
|
||||
### Roadmap
|
||||
- [ToDo](en/todo-all.md)
|
||||
- [Developers](en/developers.md)
|
||||
- [Notes from old sources](en/notes-for-resorting.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### Resources for recycling and integration
|
||||
- <https://github.com/OpenIPC/camerasrnd>
|
||||
- <https://openwrt.org/docs/techref/hardware/soc/soc.hisilicon.hi35xx>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
In Russian
|
||||
----------
|
||||
- [О проекте](ru/about.md)
|
||||
- [Установка. Шаг за шагом.](ru/installation.md)
|
||||
- [Темы для дискуссий разработчиков](ru/discussion.md)
|
||||
- [Программный переход с openipc-1.0 (OpenWrt) на openipc-2.x (Buildroot)](ru/upgrade-from-1.md)
|
||||
- [Вопросы и ответы](ru/faq.md)
|
||||
- [Хочу помочь!](ru/contribute.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### Помощь
|
||||
- [Веб-интерфейс](ru/help-webui.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### Камеры
|
||||
- [Switcam HS-303](ru/hardware-hs303.md)
|
||||
- [Ростелекомовская камера с NAND](ru/hardware-rtk-nand.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## Что можно прочитать про прошивку OpenIPC?
|
||||
- [Часто задаваемые вопросы и ответы на них][faq1]
|
||||
- [Заметки от Олега Левшина][faq3]
|
||||
|
||||
#### This is an open project, so you can help, too.
|
||||
|
||||
We try to collect, organize and share as much information regarding different
|
||||
aspects of the project as we can. But sometimes we overlook things that seem
|
||||
obvious to us, developers, but are not so obvious to end-users, people who are
|
||||
less familiar with nuts and bolts behind the scene. That is why we set up this
|
||||
wiki and let anyone having a GitHub account to make additions and improvements
|
||||
to the knowledgebase. Read [How to contribute.](en/contribute.md)
|
||||
|
||||
[faq1]: https://github.com/OpenIPC/camerasrnd/blob/master/docs/XM-FAQ-ru.md
|
||||
[faq3]: https://alarmsystem-cctv.ru/openipc-%D0%BE%D1%82%D0%BA%D1%80%D1%8B%D1%82%D1%8B%D0%B9-%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%BB%D0%BB%D0%B5%D0%BA%D1%82%D0%B8%D0%B2/
|
||||
[logo]: images/logo_openipc.png
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Оглавление](index.md)
|
||||
[Оглавление](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Прошивка OpenIPC -- что это?
|
||||
----------------------------
|
||||
|
|
@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ OpenIPC. [Список таких процессоров][socs] пока огр
|
|||
|
||||
Аккуратно снимите объектив (он держится на двух винтах) и сделайте фото матрицы.
|
||||
Одни и те же процессоры могут комплектоваться разными типами матриц, каждая из
|
||||
них требует собственного кофигурационного файла.
|
||||
них требует собственного конфигурационного файла.
|
||||
|
||||
Сделайте фотографии разъемов, чтобы не перепутать подключения, если вам
|
||||
понадобится их разъединить, например для удобного доступа к матрице. _Маленькая
|
||||
|
|
@ -69,7 +69,7 @@ UART. Как правило, это группа из трех, реже чет
|
|||
Вам нужно будет самостоятельно определить порт на плате, выяснить его
|
||||
распиновку, и либо распаять на него коннектор, либо припаять провода напрямую
|
||||
к контактам порта. Так же можно использовать прищепку с пружинными щупами для
|
||||
подключения адаптера к камере. В любом случае, соединение должно быть надежным,
|
||||
подключения адаптера к камере. В любом случае соединение должно быть надежным,
|
||||
иначе пропадание контакта во время записи/чтения может обернуться искажением
|
||||
передаваемых данных, что в свою очередь может обернуться порчей содержимого
|
||||
флэш-памяти и вывести камеру из строя. И тогда вам потребуется программатор
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Оглавление](index.md)
|
||||
[Оглавление](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Темы для дискуссий
|
||||
------------------
|
||||
|
|
@ -73,7 +73,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
* Сделать постоянно висящее сообщение о необходимости смены дефолтного пароля.
|
||||
* Разделить уровни доступа для пользователей admin (настройка сети, даты, и
|
||||
обновление стабильного релиза) и root (пролный доступ с массой диагностики).
|
||||
обновление стабильного релиза) и root (полный доступ с массой диагностики).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Фичи
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Оглавление](index.md)
|
||||
[Оглавление](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Вопросы и ответы
|
||||
----------------
|
||||
|
|
@ -52,7 +52,7 @@ mount -o nolock 95.217.179.189:/srv/ro /tmp/utils/
|
|||
/tmp/utils/ipctool
|
||||
```
|
||||
После того как утилита скачана на камеру, выполните команд `ipctool gpio scan` в терминале и пару раз закройте-откройте объектив камеры ладошкой.
|
||||
Следите за выводом ipctool чтобы определить пины, отвечающие за управление шторкой ИК фильтра.
|
||||
Следите за выводом ipctool, чтобы определить пины, отвечающие за управление шторкой ИК фильтра.
|
||||
Внесите полученные значения в настройки ночного режима Majestic. Если розовый оттенок не исчез, возможно необходимо включить инверсию сигнала сенсора.
|
||||
|
||||
Не забудьте добавить модель камеры и найденные значения GPIO в таблицу!
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Оглавление](index.md)
|
||||
[Оглавление](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Switcam HS-303
|
||||
--------------
|
||||
|
|
@ -91,7 +91,7 @@ fw_setenv sensor ov9732; reboot -f
|
|||
#### Как узнать какой IP адрес у прошитой камеры и как зайти на неё ?
|
||||
|
||||
Если внесены корректные данные по настройке WiFi интерфейса в конфигурационный
|
||||
фаил (SSID и ключ), то вы можете найти IP адрес камеры на своём роутере в списке
|
||||
файл (SSID и ключ), то вы можете найти IP адрес камеры на своём роутере в списке
|
||||
подключенных устройств с пометкой "OpenIPC".
|
||||
Интерфейс управления камерой доступен в браузере на порту 85, а доступ по SSH
|
||||
возможен на стандартном порту 22 с использованием логина root, без пароля при
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Оглавление](index.md)
|
||||
[Оглавление](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Ростелекомовская камера с NAND
|
||||
------------------------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,3 +1,6 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Оглавление](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Помощь: U-boot
|
||||
------------
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -22,7 +25,7 @@ root@openipc-hi3518ev100:~#
|
|||
|
||||
В программе-терминале, используемой для подключения к порту UART, установите
|
||||
сохранение лога сессии. В качестве примера мы используем программу-терминал
|
||||
`screen`. В этом случае команда подлючения к UART-адаптеру с сохранением лога
|
||||
`screen`. В этом случае команда подключения к UART-адаптеру с сохранением лога
|
||||
сессии в файл _fulldump.log_ будет выглядеть примерно так:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -49,7 +52,7 @@ md.b 0x0 0x800000
|
|||
md.b 0x0 0x1000000
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
После запуска команды чтения содержимого памяти вы можете отсоедить сессию,
|
||||
После запуска команды чтения содержимого памяти вы можете отсоединить сессию,
|
||||
чтобы случайное нажатие клавиш не замусорило лог. В `screen` это делается
|
||||
последовательным нажатием комбинации клавиш `Ctrl-a` и клавиши `d` (detach).
|
||||
Для последующего присоединения к запущенной сессии используйте команду
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Table of Content](index.md)
|
||||
[Оглавление](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Помощь: Веб-интерфейс
|
||||
---------------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
27
ru/index.md
27
ru/index.md
|
|
@ -1,27 +0,0 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
|
||||
Оглавление
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
- [О проекте](about.md)
|
||||
- [Установка. Шаг за шагом.](installation.md)
|
||||
- [Темы для дискуссий разработчиков](discussion.md)
|
||||
- [Программный переход с openipc-1.0 (OpenWrt) на openipc-2.x (Buildroot)](upgrade-from-1.md)
|
||||
- [Вопросы и ответы](faq.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### Помощь
|
||||
|
||||
- [Веб-интерфейс](help-webui.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### Камеры
|
||||
|
||||
- [Switcam HS-303](hardware-hs303.md)
|
||||
- [Ростелекомовская камера с NAND](hardware-rtk-nand.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## Что можно прочитать про прошивку OpenIPC?
|
||||
|
||||
* [Часто задаваемые вопросы и ответы на них][faq1]
|
||||
* [Заметки от Олега Левшина][faq3]
|
||||
|
||||
[faq1]: https://github.com/OpenIPC/camerasrnd/blob/master/docs/XM-FAQ-ru.md
|
||||
[faq3]: https://alarmsystem-cctv.ru/openipc-%D0%BE%D1%82%D0%BA%D1%80%D1%8B%D1%82%D1%8B%D0%B9-%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%BB%D0%BB%D0%B5%D0%BA%D1%82%D0%B8%D0%B2/
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Оглавление](index.md)
|
||||
[Оглавление](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Установка OpenIPC. Шаг за шагом.
|
||||
--------------------------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
19
ru/links.md
19
ru/links.md
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Оглавление](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
SoC
|
||||
---
|
||||
- https://www.augentix.com/
|
||||
- http://www.goke.com/
|
||||
- https://www.hisilicon.com/
|
||||
- http://www.ingenic.com.cn/
|
||||
- http://www.novatek.com.tw/
|
||||
- http://www.sigmastarsemi.com/
|
||||
|
||||
Полезные ссылки
|
||||
---------------
|
||||
- https://zftlab.org/
|
||||
- http://www.ipcam.xin/
|
||||
- https://ipcamtalk.com/
|
||||
- https://www.nvripc.com/
|
||||
- https://www.dvraid.com/
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Оглавление](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Хочу помочь! Что надо делать?
|
||||
-----------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Мы не откажемся от любой, даже самой малой помощи.
|
||||
Проекту нужны как те, кто читает схемы, умеет отреверсить закрытый драйвер,
|
||||
так и те, кто сможет увидеть и поправить опечатку, написать инструкцию,
|
||||
нарисовать красивую картинку или может быть даже сложить красивую песню :)
|
||||
|
||||
### Я сделал поправки в код. Как его вам прислать?
|
||||
|
||||
Для работы с кодом мы используем систему управления версиями [Git][gitdoc]
|
||||
и репозитории, расположенные на сервисе GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
Если у вас есть аккаунт на GitHub, то все просто: сделайте копию нашего
|
||||
кода в своем аккаунте (fork).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Сделайте правки в своей копии, после чего отправьте запрос на включение
|
||||
ваших изменений в нашу ветку (pull request)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Если вы по какой-то причине не пользуетесь GitHub, вы всё-равно можете
|
||||
прислать нам свои изменения в код. Для этого сделайте локальную копию
|
||||
репозитория соответствующего проекта.
|
||||
```
|
||||
git clone git@github.com:OpenIPC/firmware.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
Перенесите в него сделанные вами изменения. Запишите сделанные изменения в
|
||||
вашу локальную копию репозитория. После чего создайте патч-файл и пришлите
|
||||
его нам на адрес <dev@openipc.org>.
|
||||
```
|
||||
git format-patch master
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[gitdoc]: https://git-scm.com/book/ru/v2
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
|
|||
# Полезные ссылки
|
||||
|
||||
Железо и его производители
|
||||
--------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
### Процессоры
|
||||
|
||||
- [Ambarella](https://www.ambarella.com/)
|
||||
- [Anyka](http://www.anyka.com/)
|
||||
- [Fullhan](https://www.fullhan.com/)
|
||||
- [Goke](http://www.goke.com/)
|
||||
- [Grain Media (Novatek)](https://www.novatek.com.tw/)
|
||||
- [Hisilicon](https://www.hisilicon.com/en/)
|
||||
- [Ingenic](http://www.ingenic.com.cn/en/)
|
||||
- [MStar (MediaTek)](http://www.mstarsemi.com/)
|
||||
- [Nextchip](http://www.nextchip.com/)
|
||||
- [Novatek](https://www.novatek.com.tw/)
|
||||
- [SigmaStar](http://www.sigmastarsemi.com/)
|
||||
- [XiongmaiTech](https://www.xiongmaitech.com/)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Матрицы
|
||||
|
||||
- [Forza Silicon](https://www.forzasilicon.com/)
|
||||
- [GalaxyCore](https://en.gcoreinc.com/)
|
||||
- [OmniVision](https://www.ovt.com/)
|
||||
- [ON Semiconductor](https://www.onsemi.com/)
|
||||
- [Silicon Optronics](https://www.soinc.com.tw/)
|
||||
- [SmartSens Technology](https://www.smartsenstech.com/)
|
||||
- [Sony Semiconductor](https://www.sony-semicon.co.jp/)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Периферия
|
||||
|
||||
- [Realtek](https://www.realtek.com/)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Модули
|
||||
|
||||
- [Supertek](https://www.supertekmodule.com/)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Операционная система и программное обеспечение
|
||||
----------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- [U-Boot](https://www.denx.de/wiki/U-Boot)
|
||||
- [Buildroot](https://buildroot.org/)
|
||||
- [Bootlin](https://github.com/bootlin)
|
||||
- [HLS.js](https://github.com/video-dev/hls.js/)
|
||||
- [VLC, x264](https://www.videolan.org/)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Стандарты и прочая документация
|
||||
-------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- [MDN Web Docs](https://developer.mozilla.org/)
|
||||
- [W3cubDocs API Documentation](https://docs.w3cub.com/)
|
||||
- [MPEG-4 Standard](https://mpeg.chiariglione.org/standards/mpeg-4)
|
||||
- [MPEG-DASH: Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP](https://mpeg.chiariglione.org/standards/mpeg-dash)
|
||||
- [HLS: HTTP Live Streaming](https://developer.apple.com/streaming/)
|
||||
- [Media Source Extensions. W3C Draft](https://w3c.github.io/media-source/)
|
||||
- [Microsoft Media Foundation SDK](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/medfound/microsoft-media-foundation-sdk)
|
||||
- [Chromium MediaSource Tests](https://chromium.googlesource.com/external/w3c/web-platform-tests/+/refs/heads/master/media-source)
|
||||
|
||||
### RFC
|
||||
- [Hypertext Transfer Protocol HTTP/1.1. RFC2616](https://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc2616). Obsolete, see Obsoleted by/Updated by links.
|
||||
- [Hypertext Transfer Protocol Version 2. HTTP/2. RFC7540](https://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc7540)
|
||||
- [The Common Gateway Interface (CGI) Version 1.1. RFC3875](https://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc3875)
|
||||
- [Scripting Media Types. RFC4329](https://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc4329)
|
||||
- [JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) Pointer. RFC6901](https://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc6901)
|
||||
- [JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) Patch. RFC6902](https://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc6902)
|
||||
- [JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) Text Sequences. RFC7464](https://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc7464)
|
||||
- [The JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) Data Interchange Format. RFC8259](https://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc8259)
|
||||
- [HTTP Live Streaming. RFC8216](https://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc8216)
|
||||
- [HTTP Live Streaming, 2nd Ed. Draft](https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/draft-pantos-hls-rfc8216bis-10)
|
||||
- [Real-Time Streaming Protocol Version 2.0. RFC7826](https://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc7826)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### PTZ Protocols
|
||||
|
||||
- [Pelco](https://shopdelta.eu/pelco-d-pelco-p_l2_aid1047.html)
|
||||
- [Bosch OSRD](https://resources-boschsecurity-cdn.azureedge.net/public/documents/OSRD_Protocols_Configuration_Manual_enUS_20804604939.pdf)
|
||||
- [Bosch BiCom](https://manualzz.com/doc/22138427/bicom-protocol-for-bosch-ptz-cameras)
|
||||
- [Sony VISCA](https://www.epiphan.com/userguides/LUMiO12x/Content/UserGuides/PTZ/3-operation/VISCAcommands.htm)
|
||||
- [Panasonic AW]
|
||||
- [Panasonic WV]
|
||||
- [Samsung]
|
||||
- [LG Multix]
|
||||
- [Canon]
|
||||
- [Hitachi]
|
||||
- [AD ASCII/Manchester/RS422/RS485]
|
||||
- [LiLin]
|
||||
- [Yoko]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Технические статьи и обучающие материалы
|
||||
----------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- [REST API Tutorial](https://restfulapi.net/)
|
||||
- [Video Codec Guide](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/Media/Formats/Video_codecs)
|
||||
- [The "codecs" parameter in common media types](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/Media/Formats/codecs_parameter)
|
||||
- [Video Encoding and Playback With GStreamer (Linux)](https://developer.toradex.com/knowledge-base/video-playback-linux)
|
||||
- [Xiongmai Open Platform](https://oppf.xmcsrv.com/)
|
||||
|
||||
Интересные ресурсы
|
||||
------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- [CNX Software](https://www.cnx-software.com/)
|
||||
- [Unifore](https://www.unifore.net/)
|
||||
- [Image Sensors World](http://image-sensors-world.blogspot.com/)
|
||||
|
||||
- <https://www.goprawn.com/forum>
|
||||
- <http://www.hasecu.com/>
|
||||
- <http://www.hasecurity.com/>
|
||||
- <http://www.hlong.asia/>
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Оглавление](index.md)
|
||||
[Оглавление](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Программный переход с openipc-1.0 (OpenWrt) на openipc-2.x (Buildroot) 👻
|
||||
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
# OpenIPC Wiki
|
||||
[Оглавление](index.md)
|
||||
[Оглавление](../index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Прошивка gk7205v300 + IMX335 + XM_XT25F128B
|
||||
-------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue